The swimming abilities of water buffaloes are a fascinating aspect of their biology and behavior. These remarkable creatures are not only adept at navigating through water but also thrive in their aquatic habitats. This article delves into their swimming capabilities, the unique characteristics that enhance their swimming speed, and some intriguing facts about these animals.
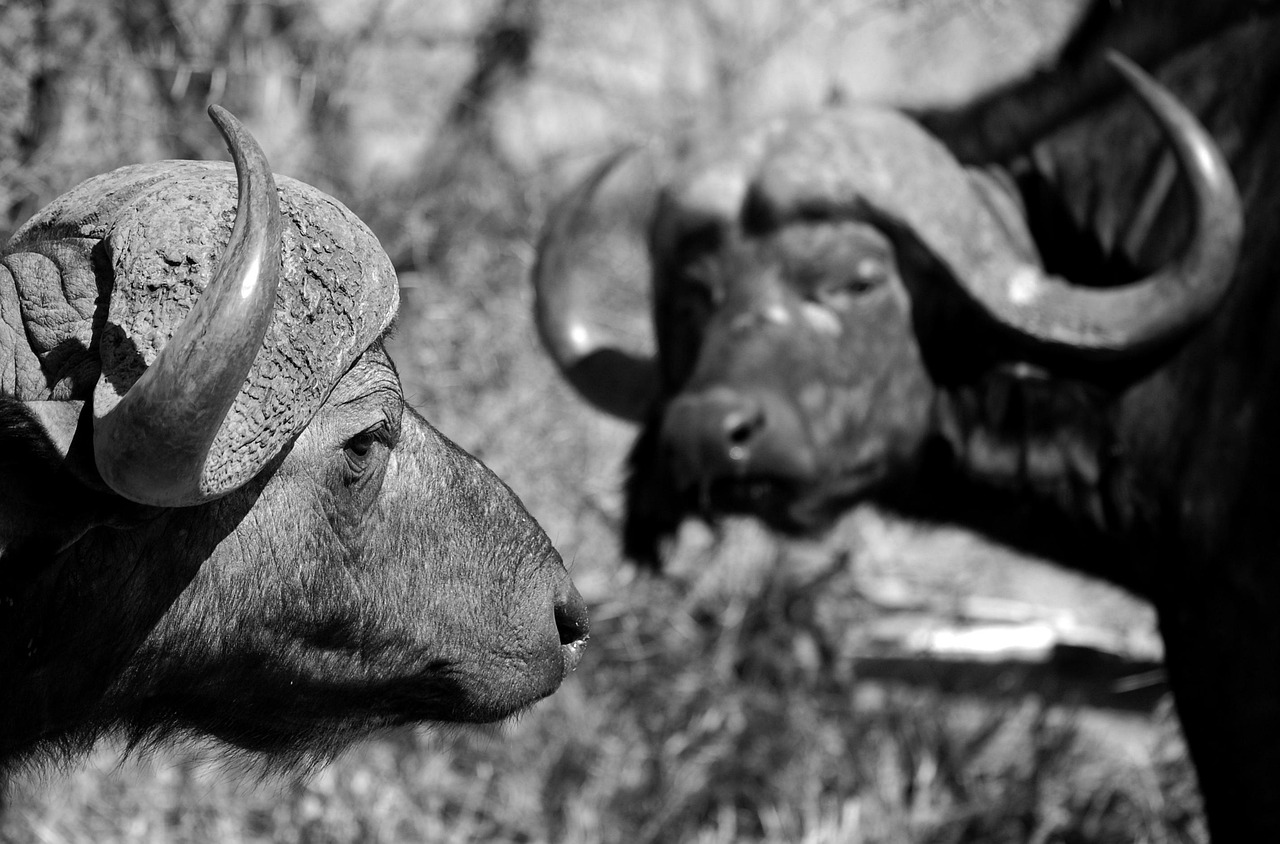
The anatomy of water buffaloes significantly influences their swimming prowess. Their muscular build and robust bodies are designed for strength, allowing them to move efficiently through water. Additionally, their long limbs and wide hooves provide stability and support while swimming.
Water buffaloes are predominantly found in warm, humid environments, particularly in wetlands, swamps, and riverbanks. These habitats not only provide them with ample water for swimming but also support their diet of aquatic vegetation. Their natural affinity for water explains their remarkable swimming behavior.
Several adaptations enable water buffaloes to excel in aquatic environments. Their bodies are naturally buoyant, allowing them to float with ease. Furthermore, their webbed hooves enhance their swimming capabilities by enabling better propulsion and maneuverability in water.
The buoyant shape of a water buffalo’s body is crucial for efficient swimming. Despite their considerable weight, this design allows them to glide through water with minimal effort, making swimming a comfortable activity.
Water buffaloes possess webbed hooves that act like paddles, providing enhanced propulsion. This adaptation not only aids in swimming but also offers stability, allowing them to navigate through various water conditions effectively.
On average, water buffaloes can swim at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour. This impressive speed is particularly notable considering their size and weight, showcasing their efficiency as swimmers.
Swimming serves multiple purposes beyond mere survival for water buffaloes; it plays a vital role in their social interactions and thermoregulation. During hot weather, these animals often seek out water to cool off, highlighting their reliance on aquatic environments.
Water buffaloes are social animals that often swim in groups. This behavior not only strengthens social bonds within herds but also provides safety in numbers as they navigate through water together.
Swimming acts as an effective cooling mechanism for water buffaloes. By immersing themselves in water, they can regulate their body temperature, which is crucial during the sweltering heat of summer months.
When examining the swimming abilities of water buffaloes in comparison to other animals, such as cattle and horses, several differences emerge. Understanding these distinctions can provide insights into their unique adaptations for life in water.
While both species can swim, water buffaloes are generally more proficient due to their specialized adaptations. Their comfort in water allows them to swim more effectively than cattle, which may struggle in aquatic environments.
Horses are also capable swimmers but lack the adaptations that water buffaloes possess. This difference gives water buffaloes an advantage in endurance and efficiency when swimming, particularly in deep or swift waters.
The conservation status of water buffaloes is critical for their survival and the preservation of their habitats. These environments are essential not only for their swimming needs but also for their overall well-being.
Water buffaloes face significant threats from habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. These factors can severely impact their swimming environments, leading to declines in their populations.
Various conservation initiatives are underway to protect water buffalo habitats. These efforts aim to ensure that these remarkable animals can continue to thrive and swim in their natural environments, preserving their unique adaptations and behaviors for future generations.

Understanding Water Buffalo Anatomy
Water buffaloes, known for their remarkable adaptability, exhibit unique anatomical features that greatly enhance their swimming capabilities. Understanding the anatomy of water buffaloes is crucial in appreciating how these animals maneuver through water with such ease and efficiency.
The physical structure of water buffaloes is specifically designed to aid in their swimming prowess. Their muscular bodies and broad frames contribute to their buoyancy, allowing them to float on water surfaces. This buoyancy is essential for conserving energy while swimming, enabling them to travel longer distances without fatigue.
One of the most significant adaptations of water buffaloes is their limb structure. Unlike many terrestrial animals, water buffaloes possess strong, sturdy legs with webbed hooves. These adaptations not only provide stability on land but also enhance their propulsion in water, making it easier for them to paddle through aquatic environments. The webbing between their hooves acts like a natural paddle, allowing for effective thrust and steering.
The overall body shape of water buffaloes is another critical factor in their swimming ability. Their rounded bodies and large lungs contribute to their buoyancy, allowing them to float effortlessly. This design minimizes drag and maximizes efficiency, enabling them to reach speeds of up to 5 miles per hour in water. The combination of their muscular build and buoyant shape makes them uniquely suited for life in aquatic habitats.
Swimming is not merely a survival skill for water buffaloes; it plays a vital role in their social behavior and environmental interactions. These animals are often seen enjoying group swims, which serve to reinforce social bonds within herds. This behavior also provides safety, as swimming in numbers can deter potential predators.
In addition to social interactions, swimming serves as an effective cooling mechanism for water buffaloes. During sweltering days, they frequently seek out water bodies to immerse themselves, helping to regulate their body temperature and avoid overheating. This behavior underscores the importance of aquatic environments in their daily lives.
Water buffaloes thrive in wetlands, swamps, and riverine environments, where their swimming abilities are put to good use. These habitats not only provide essential resources such as food and shelter but also facilitate their natural swimming behaviors. Understanding their habitats is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these remarkable creatures.
Despite their adaptability, water buffaloes face numerous threats, including habitat destruction and pollution. These factors can severely impact their swimming environments and overall population health. Conservation initiatives are essential to ensure that water buffaloes continue to thrive in their natural habitats. Protecting wetlands and river systems is key to preserving the ecosystems that support these animals.
- Water buffaloes can hold their breath underwater for several minutes, allowing them to navigate submerged areas.
- They are known to use their swimming skills to escape from predators.
- Water buffaloes are essential to many agricultural practices in Asia, often used in rice paddies where their swimming abilities are beneficial.
In conclusion, the anatomy of water buffaloes, characterized by their buoyant bodies, webbed hooves, and strong limbs, plays a significant role in their swimming abilities. Their adaptations not only enhance their efficiency in water but also contribute to their social behaviors and survival strategies in their natural habitats.

Natural Habitat of Water Buffaloes
Water buffaloes, known for their remarkable swimming abilities, are primarily found in wetlands, swamps, and riverine environments. These habitats are crucial for their survival and play a significant role in their behavior and physical adaptations. Understanding the natural habitats of water buffaloes provides insight into their affinity for water and their unique swimming behavior.
The wetlands and swamps where water buffaloes thrive are rich in vegetation and provide ample food sources, such as aquatic plants and grasses. These ecosystems not only support their dietary needs but also offer shelter from predators. The presence of water bodies allows water buffaloes to engage in their natural behaviors, including swimming, which is vital for their physical and psychological well-being.
Water buffaloes are well-adapted to their aquatic environments. One of the most notable adaptations is their buoyant body shape, which enables them to float and swim efficiently. Their large, muscular build, combined with a relatively low center of gravity, allows them to navigate through water with ease. This anatomical feature is particularly advantageous in their natural habitats, where swimming is often necessary for foraging and escaping threats.
Another adaptation that enhances their swimming capabilities is their webbed hooves. These specialized hooves provide better propulsion and stability in water, allowing water buffaloes to paddle effectively. This adaptation is crucial, especially in deeper water, where they may need to swim longer distances to reach food or safe areas.
In addition to physical adaptations, the social structure of water buffaloes influences their behavior in aquatic environments. They often swim in groups, which not only strengthens social bonds within herds but also provides safety in numbers. This behavior is particularly important in their natural habitats, where predators may be lurking nearby.
Furthermore, swimming serves as a cooling mechanism for water buffaloes during hot weather. They frequently enter water bodies to regulate their body temperature, helping them avoid overheating. This behavior is essential for their health and well-being, particularly in regions with high temperatures.
When comparing the habitats of water buffaloes with other species, it becomes evident that their preference for aquatic environments sets them apart. Unlike cattle, which may be less comfortable in water, water buffaloes are inherently drawn to it due to their adaptations. Similarly, while horses are capable swimmers, they do not possess the same physical traits that facilitate swimming as effectively as water buffaloes.
However, the natural habitats of water buffaloes face significant threats. Habitat destruction due to agricultural expansion, urbanization, and pollution poses a serious risk to their populations. These activities not only diminish their living spaces but also impact the quality of water bodies they rely on for swimming and cooling.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the natural habitats of water buffaloes. Initiatives aimed at preserving wetlands and swamps are essential for ensuring that these remarkable animals can continue to thrive in their aquatic environments. By safeguarding their habitats, we can help maintain the delicate balance of these ecosystems and support the survival of water buffaloes.
In summary, the natural habitats of water buffaloes are integral to their existence. Their adaptations for aquatic life, social behaviors, and the challenges they face highlight the importance of these environments. Understanding and protecting these habitats is essential for the future of water buffaloes and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Adaptations for Aquatic Life
Water buffaloes are remarkable creatures, particularly known for their impressive swimming abilities. Their adaptations for aquatic life are not only fascinating but also essential for their survival in their natural habitats. This section delves deeper into the specific adaptations that make water buffaloes exceptional swimmers.
Water buffaloes possess several unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in aquatic environments. These adaptations are crucial for their swimming efficiency and overall survival.
- Buoyant Bodies: One of the most significant adaptations of water buffaloes is their buoyant body structure. Their large, muscular frames are designed to float, allowing them to navigate through water with ease. This buoyancy is critical, as it reduces the energy required to swim and helps them remain afloat while resting or grazing in the water.
- Webbed Hooves: Another essential adaptation is their webbed hooves. These specially designed hooves enhance their propulsion and stability in water. The webbing between their toes acts like a paddle, enabling them to push against the water more effectively, which contributes to their swimming speed and maneuverability.
- Streamlined Body Shape: Water buffaloes have a streamlined body shape that minimizes resistance while swimming. This anatomical feature allows them to glide through water effortlessly, making their swimming both efficient and graceful.
- Strong Musculature: Their powerful muscles are not only beneficial for walking on land but also play a vital role in swimming. The strength of their limbs enables them to paddle vigorously, propelling themselves forward with impressive speed.
These adaptations are not just physical; they also reflect the behavioral aspects of water buffaloes in their natural habitats. Swimming is an integral part of their daily activities, providing them with opportunities for social interaction and relaxation.
Water buffaloes often engage in swimming as a social activity. They are known to swim in groups, which strengthens their social bonds and provides safety in numbers. This group behavior is particularly evident in the wild, where they navigate rivers and swamps together, showcasing their natural instincts.
Additionally, swimming serves as an effective cooling mechanism for water buffaloes. During hot weather, they frequently enter water bodies to regulate their body temperature. This behavior not only helps them stay cool but also allows them to escape from insects and other pests that may be bothersome on land.
When comparing water buffaloes to other animals, their swimming abilities stand out. For instance, while horses can swim, they lack the same adaptations that water buffaloes possess. The webbed hooves and buoyant bodies of water buffaloes give them an advantage in aquatic environments. Similarly, when compared to cattle, water buffaloes demonstrate greater comfort and proficiency in water, largely due to their specialized adaptations.
Understanding these adaptations highlights the water buffalo’s unique relationship with its environment. Their ability to thrive in aquatic settings is not merely a coincidence; it is a testament to their evolutionary journey and the specific pressures they have faced in their habitats.
In summary, the adaptations of water buffaloes for aquatic life are multifaceted, involving a combination of physical traits and behavioral strategies. These adaptations not only enhance their swimming abilities but also contribute to their overall survival and social structures within their herds.
Buoyancy and Body Shape
Water buffaloes are remarkable creatures, renowned for their adaptability to aquatic environments. One of the key factors that contribute to their swimming prowess is their buoyant body shape. This unique anatomical feature allows them to effortlessly float and navigate through water, making them well-suited for life in wetlands and rivers.
The body shape of water buffaloes is characterized by a broad and muscular build. This robust physique, while heavy, is designed in a way that facilitates buoyancy. Their large frames are complemented by a relatively shallow depth, which helps them maintain an optimal center of gravity while swimming. This enables them to glide through water with minimal resistance, a crucial advantage in their natural habitats.
In addition to their body shape, water buffaloes possess a layer of subcutaneous fat that enhances their buoyancy. This layer acts as a natural flotation device, allowing them to remain buoyant even while submerged. This adaptation is particularly beneficial when they are navigating through deeper waters or when they need to swim for extended periods.
Furthermore, the limb structure of water buffaloes plays a significant role in their swimming abilities. Their legs are strong and muscular, providing the necessary propulsion to move through water efficiently. The joints are flexible, allowing for a wide range of motion, which is essential for powerful strokes. Their hooves, although not webbed like those of some other aquatic animals, are broad enough to provide stability on slippery surfaces, making it easier for them to enter and exit water bodies.
The combination of these physical characteristics results in a swimming capability that is impressive for an animal of their size. Water buffaloes can swim at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour, which is quite remarkable considering their weight. This speed allows them to escape predators and travel between feeding grounds or to cooler water during hot weather.
Moreover, their buoyant bodies allow them to conserve energy while swimming. Unlike some animals that must exert considerable effort to stay afloat, water buffaloes can relax and float, using minimal energy to navigate. This energy-efficient swimming technique is essential for their survival, especially in regions where they must travel long distances in search of food and water.
In summary, the buoyant body shape and muscular build of water buffaloes are integral to their swimming efficiency. These adaptations not only enable them to thrive in aquatic environments but also play a crucial role in their overall survival. Understanding these characteristics sheds light on the fascinating relationship between water buffaloes and their natural habitats, highlighting their unique adaptations that allow them to flourish in the water.
Webbed Hooves and Propulsion
Webbed hooves are a fascinating adaptation that significantly enhances the swimming capabilities of water buffaloes. These specialized hooves provide not only better propulsion but also improved stability when navigating through water. The design of their hooves allows for a more efficient paddling motion, enabling these large animals to move swiftly and gracefully in aquatic environments.
The structure of water buffalo hooves includes a webbing between the toes, which acts like a natural paddle. This adaptation is particularly beneficial in the wetlands and swamps where these animals are commonly found. When a water buffalo enters the water, the webbed hooves spread out, increasing the surface area that comes into contact with the water. This increased surface area allows them to push against the water more effectively, resulting in enhanced propulsion.
In addition to propulsion, webbed hooves also contribute to stability while swimming. The larger surface area helps distribute the animal’s weight more evenly, preventing them from sinking too deeply and allowing for better buoyancy. This stability is crucial, especially in murky waters where visibility is low and navigating can be challenging. The ability to maintain balance and control while swimming also allows water buffaloes to forage for food and escape from potential predators.
Moreover, the adaptability of water buffaloes to their environment is evident in their swimming behavior. They are known to swim long distances, often covering several miles in search of food or to find cooler areas during hot weather. Their webbed hooves play a vital role in this endurance swimming, making it easier for them to paddle through various aquatic terrains.
Interestingly, the swimming abilities of water buffaloes are not just a result of their webbed hooves. Their overall body structure, including a strong muscular build and a buoyant shape, complements their swimming adaptations. Together, these features allow water buffaloes to thrive in their natural habitats, which often include rivers, lakes, and marshy areas.
In summary, the webbed hooves of water buffaloes are a remarkable adaptation that enhances their swimming capabilities significantly. By providing better propulsion and stability, these hooves enable water buffaloes to navigate aquatic environments with ease. As we continue to study and understand these incredible animals, it becomes clear that their adaptations are key to their survival and success in the wild.
As a testament to their swimming prowess, water buffaloes are often seen swimming alongside each other in groups, further showcasing their social nature. This group behavior not only strengthens social bonds but also provides safety in numbers while they navigate through water. Their swimming skills, combined with their adaptations, make water buffaloes truly remarkable creatures in the animal kingdom.
Swimming Speed of Water Buffaloes
Water buffaloes are remarkable creatures, not only for their size but also for their impressive swimming abilities. These animals can swim at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour, which is quite notable considering their substantial weight and size. This swimming speed allows them to navigate through various aquatic environments with ease, showcasing their adaptability and resilience.
The anatomy of water buffaloes contributes significantly to their swimming prowess. Their muscular build and unique body shape facilitate buoyancy, allowing them to float and propel themselves effectively through water. Unlike many other large mammals, water buffaloes have evolved with features that enhance their swimming capabilities, making them proficient in aquatic settings.
In their natural habitats, which include wetlands, swamps, and riverine areas, water buffaloes often find themselves in water. This affinity for aquatic environments is not just a coincidence; it is a testament to their evolutionary adaptations. Their webbed hooves provide them with better propulsion and stability while swimming, allowing them to navigate through water effortlessly. This adaptation is crucial for their survival, as it enables them to escape predators and find food in their natural habitats.
Interestingly, swimming serves more than just a survival mechanism for water buffaloes. They often engage in social swimming behaviors, typically seen swimming in groups. This social aspect strengthens bonds within their herds and provides safety in numbers, particularly when navigating potentially dangerous waters. Additionally, swimming acts as a cooling mechanism during hot weather, helping them regulate their body temperature and avoid overheating.
When comparing the swimming abilities of water buffaloes to other animals, it is evident that they possess unique advantages. For instance, while both cattle and horses can swim, water buffaloes are generally more adept due to their specialized adaptations. Horses, although capable swimmers, lack the buoyancy and webbed hooves that give water buffaloes an edge in aquatic environments. This difference highlights the evolutionary advantages that water buffaloes have developed over time.
Understanding the swimming speed and capabilities of water buffaloes also sheds light on their conservation status. These animals face numerous threats, including habitat destruction and pollution, which can severely impact their swimming environments. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these habitats, ensuring that water buffaloes can continue to thrive in their natural settings.
In conclusion, the swimming speed of water buffaloes is a fascinating aspect of their biology that illustrates their adaptability and resilience. Their ability to swim efficiently at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour, combined with their unique anatomical features, allows them to thrive in aquatic environments. By understanding these remarkable animals and their swimming behaviors, we can appreciate the importance of preserving their habitats for future generations.

Behavioral Aspects of Swimming
Swimming is an essential activity for water buffaloes, serving multiple purposes beyond mere survival. These magnificent creatures, known for their adaptability, utilize swimming as a means of social interaction, a cooling mechanism during sweltering days, and a method of navigating their aquatic habitats.
In the wild, water buffaloes often engage in social swimming behaviors. They are naturally gregarious animals, and swimming in groups helps reinforce social bonds within their herds. This communal activity not only strengthens relationships among individuals but also enhances their safety. When swimming together, they can protect one another from potential predators lurking nearby. Their synchronized movements in the water create a captivating sight, showcasing their inherent social nature.
Moreover, swimming plays a crucial role as a cooling mechanism for water buffaloes. These animals thrive in warm climates, but extreme heat can lead to overheating. To combat this, they frequently immerse themselves in water bodies, allowing them to regulate their body temperature effectively. The cool water provides relief, enabling them to maintain their energy levels and remain active throughout the day. This behavior is particularly evident during the hottest parts of the day when they seek refuge in lakes or rivers.
Additionally, water buffaloes exhibit interesting behavioral adaptations while swimming. Their buoyant bodies and webbed hooves not only aid in their swimming capabilities but also influence their behavior in water. The webbing between their hooves allows for greater propulsion, enabling them to swim efficiently and navigate through aquatic environments with ease. This anatomical feature is vital for their survival, as it helps them escape from threats and search for food in submerged vegetation.
Furthermore, swimming can also be a playful activity for water buffaloes. Young calves are often seen frolicking in the water, engaging in playful splashes and interactions with their peers. This playful behavior is crucial for their development, helping them build social skills and confidence in their aquatic environment. Such interactions foster a sense of community and contribute to the overall well-being of the herd.
In addition to these social and cooling aspects, swimming also serves as a means of foraging. Water buffaloes are known to graze on aquatic plants, and swimming allows them to access food sources that would otherwise be out of reach. By diving into the water, they can reach submerged vegetation, which is a vital part of their diet. This foraging behavior underscores the importance of swimming in their daily lives, as it directly impacts their nutrition and health.
When considering the broader implications of swimming for water buffaloes, it is essential to recognize the impact of environmental changes on their behavior. Habitat destruction and pollution threaten their natural swimming environments, which can lead to a decline in their populations. Conservation efforts are critical to ensure that these animals can continue to thrive in their aquatic habitats, where swimming plays a central role in their survival and social structure.
In summary, swimming is not merely a survival skill for water buffaloes; it encompasses a range of behavioral aspects that are integral to their social interactions, cooling mechanisms, and foraging strategies. Understanding these behaviors enhances our appreciation for these remarkable animals and highlights the importance of preserving their natural habitats.
Social Swimming Behaviors
Water buffaloes, known for their impressive swimming abilities, exhibit fascinating social behaviors when they take to the water. These animals often swim in groups, reflecting their strong social bonds and communal instincts. This behavior not only enhances their social structure but also offers significant advantages in terms of safety and navigation.
When water buffaloes swim together, they create a cohesive unit that can deter predators and enhance their sense of security. This safety in numbers principle is vital, especially in environments where they may encounter threats from larger predators or challenging water conditions. The presence of multiple buffaloes allows them to communicate effectively, using vocalizations and body language to coordinate their movements and ensure that no member of the group strays too far from the herd.
In addition to safety, swimming in groups serves as a form of social interaction. Water buffaloes engage in playful behaviors while swimming, such as splashing and nudging one another, which strengthens their social bonds. These interactions are crucial for maintaining the hierarchy within the herd and fostering relationships among individuals. Just like humans, these animals thrive on social connections, and swimming together provides an opportunity for them to reinforce these ties.
Moreover, swimming can be a relaxation activity for water buffaloes. During hot weather, they often seek out water bodies not only for cooling but also as a social space where they can engage with one another. This communal cooling off is essential for their well-being, as it helps regulate their body temperature and prevents overheating. The act of swimming together becomes a shared experience that benefits both their physical health and their social dynamics.
Interestingly, the social swimming behaviors of water buffaloes can also be observed in their migratory patterns. During seasonal changes, groups of buffaloes will often swim across rivers or lakes as they move to new grazing areas. This migration not only showcases their adaptability but also highlights the importance of their social structure during such journeys. By traveling together, they can navigate potential hazards more effectively and ensure that younger or weaker members of the herd are supported.
In conclusion, the social swimming behaviors of water buffaloes are a testament to their complex social structures and adaptability. Through group swimming, they enhance their safety, strengthen social bonds, and engage in playful interactions that contribute to their overall well-being. Understanding these behaviors not only enriches our knowledge of water buffaloes but also emphasizes the importance of preserving their natural habitats, where they can continue to thrive and exhibit these remarkable social traits.
Cooling Mechanism
Water buffaloes are remarkable creatures, known for their adaptability to various environments, particularly wetlands and riverine areas. One of the most fascinating aspects of their behavior is their swimming ability, which serves multiple purposes, including a vital during hot weather. Understanding how swimming helps regulate their body temperature can provide insights into their overall health and well-being.
During sweltering summer days, water buffaloes instinctively seek out water bodies—such as rivers, ponds, and lakes—to immerse themselves. This behavior is not merely for enjoyment; it is a crucial survival strategy. When submerged, the water helps to lower their body temperature, providing relief from the oppressive heat. The temperature regulation is essential for maintaining their metabolic functions and preventing overheating, which can lead to serious health issues.
When water buffaloes enter water, they often submerge themselves completely, with only their nostrils exposed. This behavior allows them to cool off without completely losing their ability to breathe. The cooling effect of water is significantly more efficient than simply standing in the shade or resting on dry land. The water acts as a natural air conditioner, facilitating heat dissipation through convection and evaporation.
Additionally, swimming provides water buffaloes with the opportunity to engage in social interactions. They often swim in groups, which not only strengthens social bonds within herds but also enhances their safety from predators. This social aspect is critical, as it promotes a sense of community and allows them to cooperate in finding resources.
| Benefits of Swimming for Water Buffaloes |
|---|
| Temperature Regulation |
| Social Interaction |
| Predator Avoidance |
| Exercise |
In addition to cooling off, swimming serves as a form of exercise for water buffaloes. The resistance of water requires them to use their muscles, promoting strength and endurance. This physical activity is vital for their overall health, keeping them fit and agile.
Water buffaloes are also known for their ability to adapt to different aquatic environments. Their unique anatomy, including webbed hooves and a robust body structure, enhances their swimming capabilities. These adaptations allow them to navigate through various water conditions, making them proficient swimmers.
In conclusion, the act of swimming is not just a leisure activity for water buffaloes; it is a multifaceted behavior that plays a crucial role in their survival. By utilizing water bodies to cool off, socialize, and exercise, water buffaloes demonstrate their remarkable adaptability to their environment. Understanding these behaviors highlights the importance of preserving their natural habitats, ensuring that these magnificent animals can continue to thrive in their aquatic ecosystems.

Comparison with Other Animals
When examining the swimming capabilities of various animals, particularly in comparison to water buffaloes, it becomes evident that each species has unique adaptations that influence their performance in aquatic environments. This section delves into how water buffaloes measure up against other animals such as horses and cattle, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in swimming.
Both water buffaloes and cattle possess the ability to swim, but their proficiency varies significantly. Water buffaloes are typically more adept in water due to their evolutionary adaptations. Their buoyant bodies and webbed hooves provide them with better stability and propulsion, allowing them to navigate through water with ease. In contrast, while cattle can swim, they do not exhibit the same level of comfort or efficiency. Cattle tend to struggle more in water due to their heavier body structure and lack of specialized adaptations for swimming.
Horses are known for their speed and agility on land, but when it comes to swimming, they face certain limitations. Although horses can swim effectively, they lack the buoyancy and webbing that water buffaloes possess. Water buffaloes can swim at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour, making them remarkably efficient swimmers for their size. Horses, on the other hand, are not as well adapted for aquatic environments, which can hinder their performance in water.
- Buoyancy: Water buffaloes have a naturally buoyant body shape that allows them to float effortlessly.
- Webbed Hooves: Their webbed hooves provide better propulsion and stability, making swimming easier.
- Social Swimming: Water buffaloes often swim in groups, enhancing their social bonds and safety.
Swimming serves various purposes beyond just survival for water buffaloes. It is a social activity that strengthens herd dynamics. In contrast, horses may not engage in social swimming behaviors to the same extent, often swimming alone or in smaller groups.
The habitats of these animals play a crucial role in their swimming capabilities. Water buffaloes thrive in wetlands and swamps, where they have evolved to become proficient swimmers. Horses, however, are more commonly found in diverse environments and may not have the same opportunities to develop their swimming skills.
In summary, when comparing the swimming abilities of water buffaloes with those of cattle and horses, it is clear that water buffaloes are better adapted for aquatic environments. Their unique physical characteristics and social behaviors enhance their swimming efficiency, making them exceptional swimmers among terrestrial mammals. Understanding these differences not only highlights the remarkable adaptations of water buffaloes but also emphasizes the importance of preserving their natural habitats for their continued survival.
Water Buffalo vs. Cattle
When examining the swimming capabilities of water buffaloes and cattle, it becomes clear that water buffaloes possess distinct advantages in aquatic environments. Both species are adept swimmers, yet the adaptations of water buffaloes render them more proficient in water.
Water buffaloes are equipped with several physical adaptations that enhance their swimming abilities. Their large, muscular bodies are not only strong but also buoyant, allowing them to float with ease. In contrast, cattle, while capable swimmers, do not share the same level of buoyancy. This difference is primarily due to the body composition and shape of each species.
One of the most significant adaptations of water buffaloes is their webbed hooves. These specialized hooves provide better propulsion and stability when swimming, allowing water buffaloes to navigate through water effortlessly. Cattle, on the other hand, have cloven hooves that are less effective in aquatic environments, making it more challenging for them to swim efficiently.
Water buffaloes often exhibit a natural affinity for water, frequently engaging in swimming as a social activity. They are known to swim in groups, which not only enhances their social bonds but also provides safety in numbers while navigating through water bodies. Cattle, while they can swim, tend to avoid water unless absolutely necessary, making their swimming behavior less social and more instinctual.
Water buffaloes thrive in wetland and swamp environments, which are integral to their lifestyle. Their comfort in these habitats allows them to engage in swimming as a regular activity, whether for cooling off or foraging. Cattle, conversely, are less inclined to enter water, primarily due to their evolutionary background and habitat preferences.
When it comes to swimming speed, water buffaloes can reach speeds of up to 5 miles per hour. This impressive speed is particularly notable given their size and weight. Cattle can swim as well, but typically at slower speeds and with less efficiency, further emphasizing the advantages of water buffaloes in aquatic settings.
Both species are affected by their environments, but water buffaloes are particularly dependent on healthy aquatic habitats. Pollution and habitat destruction pose significant threats to their swimming environments. Cattle, while less reliant on water bodies, also face challenges from environmental changes that can impact their overall health and behavior.
Understanding the differences in swimming capabilities between water buffaloes and cattle is crucial for conservation efforts. Protecting the natural habitats of water buffaloes ensures that they can continue to thrive and swim effectively. Conservation initiatives focused on wetlands and riverine environments are essential for the survival of these remarkable animals.
In conclusion, while both water buffaloes and cattle possess swimming abilities, the adaptations of water buffaloes make them more proficient swimmers. Their unique physical features, behavioral patterns, and comfort in aquatic environments set them apart, highlighting the importance of preserving their habitats for future generations.
Water Buffalo vs. Horses
When it comes to swimming, different animals exhibit varying degrees of proficiency, and the comparison between water buffaloes and horses highlights these differences remarkably. While both species are capable swimmers, their anatomical adaptations and behavioral tendencies create distinct advantages for each in aquatic environments.
Water Buffalo Swimming Capabilities
Water buffaloes are well-adapted to life in and around water. Their buoyant bodies and webbed hooves allow them to swim with relative ease. These adaptations provide them with the necessary stability and propulsion to navigate through water efficiently. In fact, water buffaloes can achieve swimming speeds of up to 5 miles per hour, which is impressive considering their substantial size and weight.
Horses and Their Swimming Skills
On the other hand, horses are also capable swimmers, but their adaptations are not as specialized for aquatic life. Horses possess a different body structure, with a more elongated shape and a less buoyant build. This means that while they can swim, they do so with less efficiency compared to water buffaloes. Horses tend to rely more on their strong legs to paddle through water, which can be taxing over longer distances.
Comparative Adaptations
- Body Structure: Water buffaloes have a stockier, more muscular build that aids in swimming, while horses have a leaner, more athletic frame.
- Hoof Design: The webbed hooves of water buffaloes provide better grip and propulsion in water, whereas horses have solid hooves that are not as effective for swimming.
- Endurance: Water buffaloes are more suited for prolonged swimming due to their adaptations, making them ideal for navigating rivers and swamps.
Behavioral Differences in Swimming
Another critical aspect to consider is the behavioral tendencies of these animals while swimming. Water buffaloes often swim in groups, which not only enhances their safety but also serves as a social activity that reinforces herd bonds. In contrast, horses may swim alone or in smaller groups, and their swimming is often more of a necessity than a social interaction.
Environmental Factors
The environments in which these animals typically swim also play a significant role in their swimming behavior. Water buffaloes thrive in wetlands and swamps, which are their natural habitats. These areas provide ample opportunities for swimming and cooling off, especially during hot weather. Horses, while they can swim in various bodies of water, do not have the same affinity for aquatic environments as water buffaloes.
Conclusion on Swimming Proficiency
In summary, while both water buffaloes and horses are capable swimmers, the adaptations of water buffaloes give them a distinct advantage in aquatic environments. Their specialized body structure, webbed hooves, and social swimming behaviors enable them to navigate water with greater efficiency and endurance. Understanding these differences not only highlights the unique characteristics of each species but also underscores the importance of their respective habitats in supporting their swimming abilities.
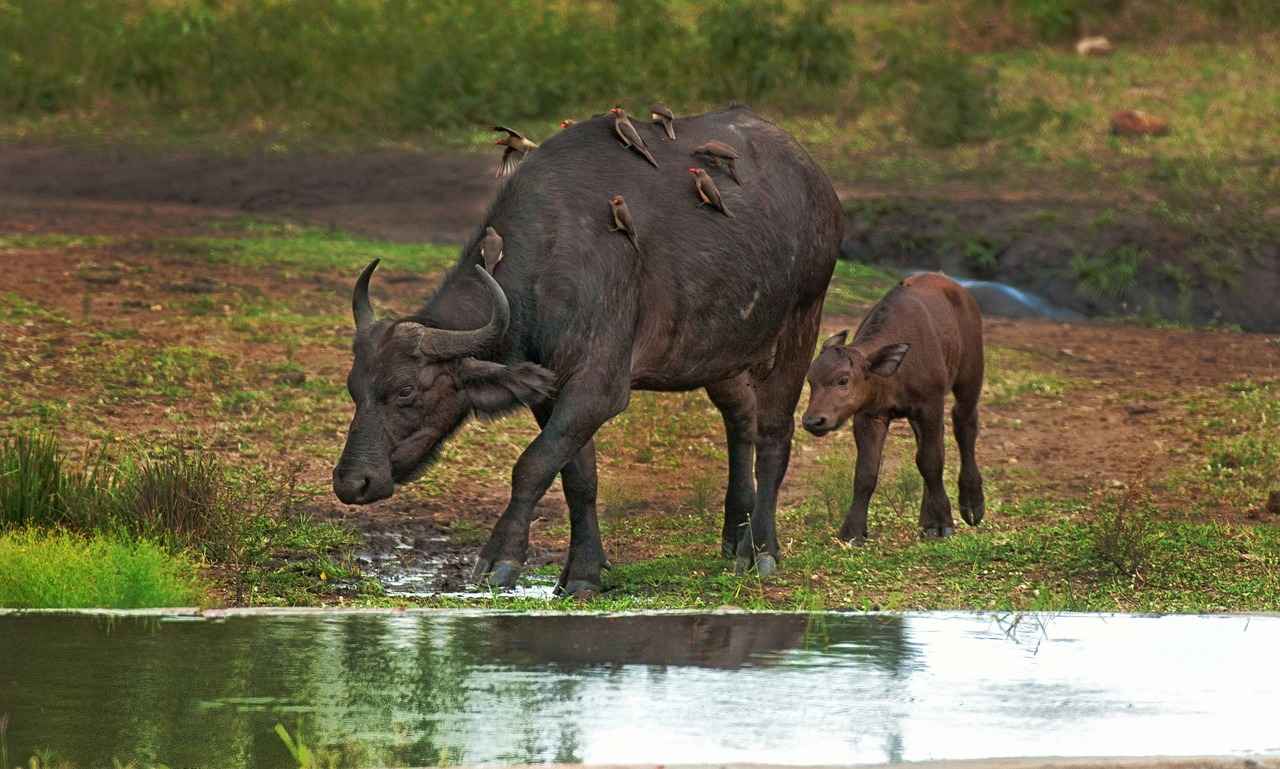

Conservation Status and Swimming Habitats
The conservation status of water buffaloes is a critical aspect of understanding their future and the preservation of their aquatic habitats. These habitats are not only essential for their swimming abilities but also play a vital role in their overall survival. As a domesticated species, water buffaloes are integral to the agricultural practices of many cultures, yet their natural populations face numerous challenges.
Water buffaloes thrive in wetlands, swamps, and riverine environments. These areas provide not only food resources but also the necessary conditions for swimming, which is an important behavior for thermoregulation and social interaction. The preservation of these habitats is crucial as they serve as breeding grounds and safe spaces for the buffaloes.
The conservation status of water buffaloes varies globally. In some regions, they are considered domesticated and face less threat, while in others, wild populations are endangered. According to the IUCN Red List, habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock have significantly impacted their populations.
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization and agricultural expansion lead to the loss of wetlands.
- Pollution: Contaminants from industrial and agricultural runoff affect water quality.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns can disrupt the delicate ecosystems that support water buffaloes.
To combat these threats, various conservation efforts are underway. Organizations are working to:
- Restore degraded habitats to support water buffalo populations.
- Implement sustainable agricultural practices that minimize environmental impact.
- Raise awareness about the importance of water buffaloes in local ecosystems.
Water buffaloes play a significant role in their ecosystems. As they swim and graze, they help maintain the health of aquatic environments. Their activities promote biodiversity and contribute to the balance of their habitats. Protecting these animals also means safeguarding the intricate web of life that depends on them.
Local communities are often at the forefront of conservation efforts. By engaging in sustainable practices and understanding the ecological value of water buffaloes, they can help protect these animals and their habitats. Education programs aimed at local farmers and stakeholders are essential for fostering a sense of responsibility and stewardship.
In summary, the conservation status of water buffaloes is not just about protecting a species; it is about preserving the ecosystems that support them. Their ability to swim and thrive in aquatic environments is closely linked to the health of these habitats. By prioritizing conservation efforts and community involvement, we can ensure a future where water buffaloes continue to flourish in their natural settings.
Threats to Their Habitat
Water buffaloes are magnificent creatures that play a significant role in their ecosystems. However, they are currently facing numerous challenges that threaten their habitats and, consequently, their survival. Understanding these threats is crucial for the conservation of this remarkable species.
Water buffaloes are increasingly vulnerable due to habitat destruction and pollution. These factors can have severe impacts on their swimming environments and overall population health, making it essential to address these issues.
- Habitat Destruction: One of the primary threats to water buffalo habitats is the conversion of wetlands and swamps into agricultural land. As human populations grow, the demand for farmland increases, leading to the drainage of vital aquatic ecosystems. This not only reduces the available swimming areas for water buffaloes but also disrupts the delicate balance of their natural habitats.
- Pollution: Water pollution is another critical issue affecting water buffaloes. Agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and plastic pollution contaminate the water sources that buffaloes rely on for swimming and drinking. Polluted water can lead to health issues for these animals, including skin diseases and internal ailments, ultimately impacting their survival rates.
- Climate Change: The effects of climate change are also becoming increasingly apparent. Rising temperatures can lead to the drying up of wetlands, reducing the areas where water buffaloes can swim and cool off. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, can further disrupt their habitats.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: As urban areas expand, water buffaloes often find themselves in conflict with human activities. Encroachment on their habitats can lead to competition for resources and increased mortality rates due to accidents or direct human intervention.
The loss of habitat has dire consequences for water buffalo populations. Without access to adequate swimming environments, these animals may struggle to regulate their body temperature, leading to stress and health problems. Furthermore, diminished habitats can result in decreased food availability, which is vital for their overall health and reproductive success.
Recognizing the threats faced by water buffaloes, various conservation efforts are underway globally. Organizations are working to restore wetlands and protect existing habitats through sustainable practices. These initiatives aim to create a balance between agricultural needs and the preservation of natural ecosystems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas where water buffaloes can thrive without human interference is crucial. These zones help maintain biodiversity and provide safe swimming environments.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential. Educating farmers about sustainable practices can reduce habitat destruction while promoting coexistence with wildlife.
- Pollution Control: Implementing stricter regulations on waste disposal and promoting cleaner agricultural practices can significantly reduce pollution levels in water sources, benefiting both water buffaloes and other wildlife.
In conclusion, the threats to water buffalo habitats are multifaceted and require urgent attention. By understanding these challenges and supporting conservation initiatives, we can help ensure the survival of water buffaloes and the preservation of their aquatic environments for generations to come.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in safeguarding the future of water buffaloes, ensuring that these magnificent creatures can thrive in their natural habitats. As the demand for land and water resources increases, the habitats of water buffaloes face significant threats. To combat this, various initiatives are being implemented globally, focusing on habitat preservation, sustainable farming practices, and raising awareness about the importance of these animals.
One of the primary conservation efforts involves the preservation of wetlands and riverine ecosystems where water buffaloes naturally reside. These environments are essential not only for the buffaloes but also for a myriad of other wildlife species. Organizations are working to establish protected areas and wildlife reserves, ensuring that these habitats remain intact and free from industrial development and pollution.
Many water buffaloes are domesticated and play a significant role in agriculture. Promoting sustainable farming practices is vital to ensure that farming does not encroach on their natural habitats. This includes implementing rotational grazing, reducing pesticide use, and encouraging organic farming methods. By doing so, the health of the ecosystems where water buffaloes live can be maintained, allowing them to flourish.
Engaging local communities is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. Educational programs are being developed to raise awareness about the ecological importance of water buffaloes and their habitats. By involving communities in conservation, individuals can learn to value these animals not only for their agricultural benefits but also for their role in maintaining biodiversity.
Scientific research plays a pivotal role in conservation strategies. Ongoing studies are focused on understanding the behavior, population dynamics, and health of water buffaloes in the wild. Monitoring programs help track changes in their populations and habitats, enabling conservationists to adapt their strategies as needed. This data is essential for making informed decisions about conservation policies.
Collaboration between non-governmental organizations (NGOs), governmental bodies, and local communities enhances the effectiveness of conservation efforts. Many NGOs are dedicated to the protection of water buffaloes and their habitats, working alongside governments to develop policies that support conservation. These partnerships are vital for pooling resources, expertise, and funding to implement successful initiatives.
Raising global awareness about the plight of water buffaloes is another critical aspect of conservation. Campaigns aimed at highlighting the threats these animals face, such as habitat loss and climate change, can mobilize support and funding for conservation projects. Social media, documentaries, and educational materials are powerful tools for spreading awareness and fostering a sense of responsibility towards wildlife conservation.
Advocating for strong legislation to protect water buffalo habitats is essential. Conservationists work to influence policy decisions that impact land use and environmental regulations. By establishing legal protections for critical habitats, the long-term survival of water buffaloes can be secured. Effective policies can mitigate the effects of pollution, deforestation, and other activities that threaten their ecosystems.
In conclusion, the conservation of water buffaloes and their habitats is a multifaceted effort requiring collaboration, education, and sustainable practices. By implementing these strategies, we can ensure that future generations will be able to witness the beauty of these remarkable animals swimming in their natural environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How fast can a water buffalo swim?
Water buffaloes can swim at impressive speeds, typically reaching up to 5 miles per hour. Given their size and weight, this is quite remarkable!
- What adaptations help water buffaloes swim?
Water buffaloes have several adaptations for swimming, including buoyant body shapes and webbed hooves. These features allow them to navigate water effortlessly.
- Where do water buffaloes typically live?
Water buffaloes are primarily found in wetlands, swamps, and riverine environments. These habitats are crucial for their swimming behavior and overall well-being.
- Do water buffaloes swim alone or in groups?
Water buffaloes often swim in groups, which strengthens social bonds and provides safety in numbers while navigating through water.
- How do water buffaloes regulate their body temperature?
Swimming acts as a cooling mechanism for water buffaloes. During hot weather, they often enter water bodies to help regulate their body temperature and avoid overheating.
- Are water buffaloes more proficient swimmers than cattle?
Yes, water buffaloes are generally more comfortable and proficient swimmers than cattle due to their unique adaptations for aquatic life.
- What are the conservation concerns for water buffaloes?
Water buffaloes face threats from habitat destruction and pollution, which can significantly impact their swimming environments and overall population health.