This article delves into effective methods for rapidly losing water weight, including dietary changes, exercise routines, and lifestyle adjustments. Discover scientifically-backed strategies for achieving quick results while maintaining health.
Understanding Water Weight
Water weight refers to the excess fluid retained in the body, which can fluctuate due to various factors. Understanding its causes is crucial for implementing effective weight loss strategies.
Common Causes of Water Retention
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menstrual cycles or pregnancy, can lead to significant water retention.
- Dietary Choices: High sodium and processed food intake can exacerbate fluid retention.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, such as kidney or heart problems, may also contribute to increased water retention.
Effective Dietary Changes
Making specific dietary changes can help reduce water retention quickly. Here are some strategies:
- Reducing Sodium Intake: Lowering sodium consumption is essential for minimizing water retention. Processed foods often contain high levels of sodium, so opting for fresh, whole foods can be beneficial.
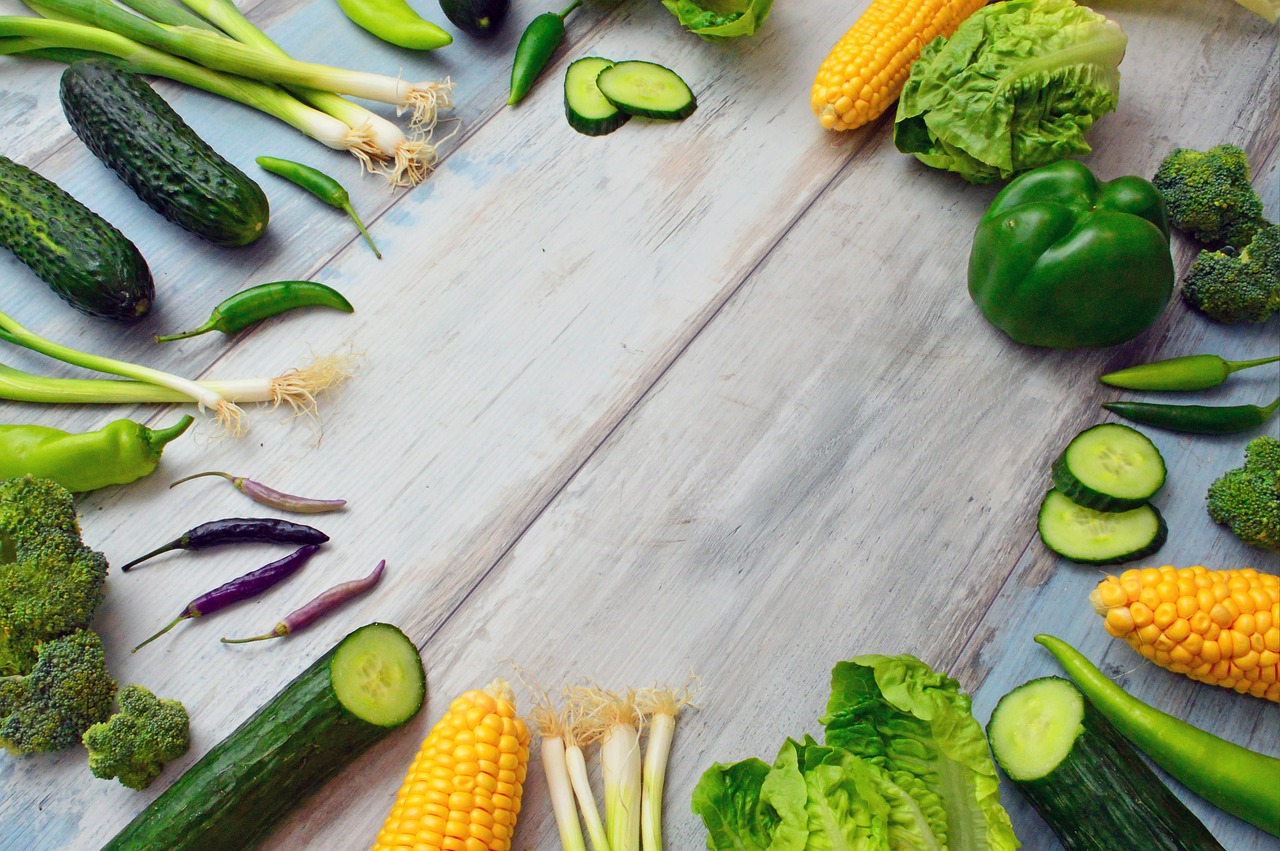
- Incorporating Diuretic Foods: Foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and asparagus act as natural diuretics, helping to flush excess water from the body.
The Role of Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance of fluids in the body. Ironically, drinking more water can help reduce water retention.
- Benefits of Increased Water Intake: Drinking adequate water can signal the body to release stored fluids, counteracting water retention.
- Hydration and Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances circulation and promotes sweating, which can help expel excess water.
Physical Activity and Water Weight Loss
Engaging in regular exercise is a powerful strategy for losing water weight. Different types of workouts can yield varying results in fluid loss.
- Aerobic Exercise for Quick Results: Aerobic activities, such as running or cycling, can lead to immediate water loss through sweat.
- Strength Training: While strength training may not produce immediate water loss, it helps build muscle, which can enhance metabolism and promote long-term weight management.
Additional Lifestyle Adjustments
Incorporating lifestyle changes can further support efforts to lose water weight. Simple adjustments can lead to significant improvements in overall fluid balance.
- Avoiding Tight Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can help improve circulation and reduce the feeling of bloating associated with water retention.
- Managing Stress Levels: High stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances that lead to water retention. Practicing stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy fluid balance.
Conclusion
By understanding the causes of water retention and implementing these effective strategies, individuals can achieve rapid water weight loss while preserving overall health. Combining dietary changes, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments can create a holistic approach to managing water weight effectively.

Understanding Water Weight
is essential for anyone looking to manage their weight effectively. Water weight refers to the excess fluid retained in the body, which can fluctuate due to various factors. This retention can lead to temporary increases in weight and can be influenced by a range of physiological and lifestyle factors. By understanding these causes, individuals can implement effective strategies to address water retention and achieve their weight loss goals.
Water weight is not a reflection of fat gain; rather, it is a result of the body holding onto excess fluids. This phenomenon can be caused by hormonal changes, dietary choices, and even specific medical conditions. Recognizing the underlying reasons for water retention can aid in developing targeted solutions for rapid weight loss.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, particularly those associated with the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can lead to significant water retention. These fluctuations may cause women to experience noticeable weight changes at different times of the month.
- Dietary Influences: The foods we consume play a crucial role in fluid retention. Diets high in sodium can lead to increased water retention, while foods rich in potassium can help balance sodium levels and promote fluid loss.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, such as heart or kidney problems, can lead to chronic water retention. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if water retention is persistent or accompanied by other symptoms.
By identifying these common causes of water retention, individuals can better manage their weight. For instance, understanding the impact of dietary choices can empower individuals to make healthier food selections that promote fluid balance.
Incorporating diuretic foods into the diet is one practical strategy for reducing water weight. Foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and asparagus can naturally help the body expel excess fluids. Additionally, maintaining proper hydration is counterintuitive but essential; drinking adequate water signals the body to release stored fluids, thus reducing water retention.
Regular physical activity is another effective approach to combat water weight. Engaging in aerobic exercises like running, cycling, or swimming can promote sweating, leading to immediate fluid loss. Strength training, while not as effective for immediate water loss, helps build muscle mass, which can enhance overall metabolism and support long-term weight management.
Moreover, lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact water retention. For example, wearing loose-fitting clothing can improve circulation and reduce feelings of bloating. Stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also help regulate hormonal levels, thereby minimizing water retention.
In summary, understanding water weight and its causes is crucial for anyone looking to manage their weight effectively. By making informed dietary choices, engaging in regular physical activity, and implementing lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively address water retention and achieve their weight loss goals. Remember, the journey to a healthier body is not just about losing weight but also about maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle.

Common Causes of Water Retention
Water retention, also known as edema, can be a frustrating issue for many individuals. Understanding the common causes of water retention is essential for effectively addressing the problem and finding suitable solutions. This section delves into the various factors that lead to fluid retention in the body, helping you identify potential triggers and take proactive measures.
One of the most significant contributors to water retention is hormonal fluctuations. These changes can occur due to various life stages, including:
- Menstrual Cycle: Many women experience increased water retention during their menstrual cycle due to hormonal shifts, particularly with estrogen and progesterone levels. This can lead to temporary weight gain and bloating.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous hormonal changes, which can result in fluid retention as the body prepares to support the developing fetus. This is a normal physiological response, but it can still be uncomfortable.
- Menopause: As women reach menopause, hormonal changes can lead to increased water retention, making it essential to monitor dietary and lifestyle choices during this transition.
Your dietary habits play a crucial role in water retention. A diet high in sodium can cause the body to hold onto excess fluid. Here are some dietary factors to consider:
- Sodium Consumption: Processed foods and restaurant meals often contain high levels of sodium, which can lead to increased water retention. Reducing sodium intake by opting for fresh, whole foods can significantly alleviate this issue.
- Carbohydrate Intake: High-carb diets can also lead to temporary water retention. When carbohydrates are stored as glycogen, they bind with water, causing the body to retain more fluid.
- Dehydration: Ironically, not drinking enough water can lead to water retention. When the body is dehydrated, it tends to hold onto fluids, resulting in a bloated feeling.
Several underlying medical conditions can contribute to water retention. Recognizing these can help in seeking appropriate treatment:
- Heart Conditions: Conditions such as congestive heart failure can cause the body to retain fluids as the heart struggles to pump effectively.
- Kidney Issues: The kidneys play a vital role in regulating fluid balance. If they are not functioning correctly, it can lead to fluid retention.
- Liver Disease: Liver conditions can disrupt normal fluid regulation, resulting in edema.
In addition to hormonal changes and dietary choices, certain lifestyle factors can also lead to water retention:
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to poor circulation, which may exacerbate fluid retention in the lower extremities.
- Stress: High-stress levels can lead to hormonal imbalances that trigger water retention. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga can be beneficial.
- Climate: Hot weather can cause the body to retain water as a natural response to prevent dehydration.
By understanding these common causes of water retention, individuals can take targeted actions to mitigate fluid retention and improve their overall well-being. Recognizing the interplay between hormones, diet, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors is crucial for effective management.
Hormonal Fluctuations
play a significant role in water retention, particularly in women during specific life stages such as the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. These natural changes in hormone levels can lead to noticeable variations in body weight due to fluid retention. Understanding these patterns is crucial for managing expectations and developing effective strategies for weight management.
During the menstrual cycle, hormonal shifts—primarily involving estrogen and progesterone—can cause the body to retain more water. This phenomenon is often most pronounced in the days leading up to menstruation, when progesterone levels peak. As a result, many women experience increased bloating and weight gain, which can be disheartening if they are trying to lose weight. Recognizing that these changes are temporary and linked to hormonal activity can help women plan their weight loss efforts more effectively.
Similarly, pregnancy introduces a host of hormonal changes that can significantly affect fluid retention. The body retains more water to support the growing fetus, which is a normal physiological response. This increase in water retention can lead to noticeable weight gain, but it is important for expectant mothers to understand that this is not solely fat gain. Instead, it is primarily due to the body’s need for extra fluids and nutrients. Awareness of this can help differentiate between healthy weight gain and excess water weight, alleviating unnecessary concern.
Aside from these life stages, hormonal fluctuations can also be influenced by other factors such as stress, diet, and certain medications. For instance, stress can elevate cortisol levels, which may lead to increased water retention as the body responds to perceived threats. Additionally, certain medications, particularly those related to hormonal therapies or contraceptives, can also affect fluid balance in the body.
To manage water retention caused by hormonal fluctuations, individuals can adopt several strategies:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can actually help reduce water retention by signaling the kidneys to release excess fluids.
- Monitor Sodium Intake: Reducing sodium consumption can help minimize water retention, as sodium can cause the body to hold onto fluids.
- Incorporate Diuretic Foods: Foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and asparagus can act as natural diuretics, helping to flush excess water from the body.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in physical activity can promote sweating and improve circulation, both of which help to reduce water retention.
- Manage Stress: Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation can help maintain hormonal balance and reduce the risk of water retention.
By understanding the impact of hormonal fluctuations on water retention, individuals can better manage their weight and health. Awareness of these patterns not only aids in setting realistic expectations regarding weight changes but also empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their weight management journey. Ultimately, recognizing that water retention is a natural response to hormonal changes can alleviate stress and promote a healthier relationship with one’s body.
Menstrual Cycle Effects
The menstrual cycle is a natural process that many women experience, and it often comes with a variety of physical and emotional changes. One of the less discussed effects of the menstrual cycle is water retention, which can significantly impact a woman’s weight and overall comfort. Understanding the underlying causes of this phenomenon can be beneficial for women looking to manage their weight effectively.
During the menstrual cycle, hormonal fluctuations, particularly in estrogen and progesterone levels, can lead to increased water retention. This is especially common in the luteal phase, which occurs after ovulation and before menstruation. During this time, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy, and hormonal changes can cause the body to retain more fluids.
Women may notice several symptoms associated with water retention during their menstrual cycle, including:
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
- Weight Fluctuations: Temporary increases in weight due to excess fluid.
- Swelling in Extremities: Hands and feet may feel puffy or swollen.
Understanding that water retention is a normal part of the menstrual cycle can help alleviate concerns about sudden weight gain. Here are some effective strategies to manage this condition:
Making certain dietary changes can help alleviate water retention. Reducing sodium intake is crucial, as high sodium levels can exacerbate fluid retention. Instead, focus on incorporating potassium-rich foods, such as bananas and spinach, which can help balance sodium levels and promote fluid balance.
It may seem counterintuitive, but drinking more water can actually help reduce water retention. When the body is adequately hydrated, it is less likely to hold onto excess fluids. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, especially during your menstrual cycle.
Engaging in regular exercise can also help reduce water weight. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, running, or cycling, can promote sweating, which helps expel excess fluids. Additionally, strength training can build muscle, which increases metabolism and aids in long-term weight management.
Some women find relief from water retention through herbal diuretics, such as dandelion or green tea. These can help the body release excess fluids naturally. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
High stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may worsen water retention. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help maintain a healthy hormonal balance and reduce the likelihood of fluid retention.
In summary, water retention during the menstrual cycle is a common occurrence influenced by hormonal changes. By understanding the causes and implementing effective management strategies, women can mitigate the effects of water retention and maintain a healthier balance during their cycle. Recognizing that these changes are temporary can also help in managing expectations and emotional well-being.
Pregnancy and Water Retention
Pregnancy is a remarkable journey that brings about numerous changes in a woman’s body. One of the most common physiological responses during this time is increased fluid retention. This phenomenon can be attributed to several factors, including hormonal fluctuations, increased blood volume, and the body’s efforts to support the developing fetus.
Understanding the nature of water retention during pregnancy is crucial for expecting mothers. It allows them to differentiate between healthy weight gain and excess water weight, which can often lead to discomfort and health concerns. Fluid retention is typically more pronounced in the later stages of pregnancy, as the body adapts to accommodate the growing baby.
Several key factors contribute to water retention during pregnancy:
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy hormones, particularly progesterone, can lead to increased fluid retention. These hormones cause the body to hold onto more water, which is necessary for supporting the baby.
- Increased Blood Volume: As the pregnancy progresses, a woman’s blood volume increases significantly to supply oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. This increase can also result in more fluid being retained in the tissues.
- Pressure from the Growing Uterus: The expanding uterus can exert pressure on blood vessels, particularly in the pelvic area. This pressure can impede blood flow and lead to fluid accumulation in the lower extremities.
It is essential for pregnant women to recognize what constitutes healthy weight gain. The Institute of Medicine provides guidelines based on pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). For instance, women with a normal BMI should aim for a weight gain of about 25 to 35 pounds throughout their pregnancy. However, much of this weight gain is not solely attributed to fat but includes:
- The growing fetus
- Amniotic fluid
- Increased breast tissue
- Placental weight
- Increased blood volume
While some weight gain is expected, excessive fluid retention can lead to conditions such as edema. This occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues, particularly in the legs, ankles, and feet, causing swelling and discomfort. If swelling is accompanied by sudden weight gain, headaches, or visual disturbances, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider to rule out conditions like preeclampsia.
There are several strategies that pregnant women can adopt to manage water retention effectively:
- Stay Hydrated: Ironically, drinking more water can help reduce fluid retention. Proper hydration encourages the body to release excess fluids and can alleviate swelling.
- Monitor Sodium Intake: Reducing sodium consumption can significantly impact fluid retention. Processed foods are often high in sodium, so opting for fresh, whole foods can help.
- Elevate Your Feet: Taking breaks to elevate the feet can improve circulation and reduce swelling in the lower extremities.
- Exercise Regularly: Gentle physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can promote circulation and help manage water retention.
In conclusion, while water retention is a common occurrence during pregnancy, understanding its causes and recognizing the signs of healthy weight gain can empower women to manage their health effectively. By adopting simple lifestyle changes and remaining informed, expecting mothers can navigate this transformative period with confidence and comfort.
Dietary Influences on Water Retention
Diet plays a vital role in water retention, with high sodium intake being a primary culprit. Adjusting dietary habits can lead to significant reductions in water weight. Understanding how food choices impact fluid balance is essential for anyone looking to manage their weight effectively.
One of the most significant contributors to water retention is sodium. Sodium is an essential mineral that helps regulate fluid balance in the body. However, excessive sodium consumption can lead to the body retaining more water than necessary. Processed foods, such as canned soups, deli meats, and snack foods, often contain high levels of sodium, making them a primary source of this issue.
To combat water retention, it is crucial to reduce sodium intake. This can be achieved by:
- Choosing fresh foods: Opt for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, which are naturally low in sodium.
- Reading labels: Always check food labels for sodium content, aiming for options that contain less than 140 mg of sodium per serving.
- Cooking at home: Preparing meals from scratch allows you to control the amount of salt added to your dishes.
In addition to managing sodium intake, incorporating diuretic foods into your diet can also help reduce water retention. Diuretic foods are those that promote the production of urine, helping to expel excess fluids. Some effective diuretic foods include:
- Cucumbers: High in water content and low in calories, cucumbers can help flush out excess fluids.
- Asparagus: Contains asparagine, an amino acid that acts as a natural diuretic.
- Watermelon: Rich in water and potassium, watermelon helps balance sodium levels and reduce bloating.
- Celery: Contains compounds that can help relax blood vessels and promote fluid excretion.
Another important aspect of managing water retention is hydration. Ironically, drinking more water can actually help reduce water retention. When the body is dehydrated, it tends to hold onto fluids. By increasing water intake, you can signal your body to release stored fluids. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day, adjusting based on your activity level and climate.
Moreover, regular physical activity can significantly aid in reducing water retention. Exercise helps improve circulation and encourages sweating, which can lead to the loss of excess water. Incorporating both aerobic exercises, like running or cycling, and strength training into your routine can yield optimal results.
In summary, dietary influences play a crucial role in water retention. By reducing sodium intake, incorporating diuretic foods, staying well-hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise, you can effectively manage your body’s fluid balance. These changes not only help with water weight loss but also promote overall health and well-being.

Effective Dietary Changes
Making specific dietary changes can significantly aid in reducing water retention. By focusing on hydration and incorporating nutrient-rich foods, individuals can promote a healthier balance within their bodies. This section delves into the most effective dietary strategies to combat water retention quickly and efficiently.
Understanding the Impact of Sodium
One of the primary contributors to water retention is a high intake of sodium. Sodium causes the body to hold onto excess fluid, leading to bloating and discomfort. To mitigate this, it is essential to:
- Reduce processed food consumption, as these often contain high sodium levels.
- Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables that are naturally low in sodium.
- Use herbs and spices for flavoring instead of salt.
Incorporating Diuretic Foods
Another effective strategy is to include diuretic foods in your diet. These foods help stimulate urine production, aiding in the elimination of excess water. Some of the most beneficial diuretic foods include:
- Cucumbers: High in water content and low in calories.
- Watermelon: Known for its hydrating properties and ability to flush out excess fluids.
- Asparagus: Contains asparagine, a natural diuretic that promotes fluid balance.
- Celery: Rich in potassium, which helps balance sodium levels in the body.
Emphasizing Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated is counterintuitive but crucial for reducing water retention. Drinking sufficient water can signal the body to release stored fluids, effectively combating retention. Aim for:
- At least 8-10 glasses of water daily to maintain optimal hydration levels.
- Incorporate herbal teas, which can also provide hydration and additional health benefits.
The Role of Potassium
Potassium is another essential nutrient that plays a vital role in fluid balance. It helps counteract the effects of sodium and can promote the excretion of excess water. Foods rich in potassium include:
- Bananas
- Sweet potatoes
- Spinach
- Avocados
Avoiding Excess Sugar
High sugar intake can also contribute to water retention. Sugary foods can lead to increased insulin levels, which may cause the body to retain more sodium. To combat this, consider:
- Limiting sugary snacks and beverages.
- Choosing whole fruits over fruit juices or sugary desserts.
Timing Your Meals
Meal timing can also influence water retention. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent insulin spikes, which may contribute to fluid retention. Aim for:
- Three balanced meals with healthy snacks in between.
- Incorporating fiber-rich foods to promote digestive health.
Conclusion
Incorporating these dietary changes can lead to a significant reduction in water retention. By focusing on hydration, reducing sodium, and including diuretic foods, individuals can achieve a healthier fluid balance in their bodies. Remember, consistency is key, and making these changes a part of your daily routine will yield the best results.
Reducing Sodium Intake
is a fundamental strategy for those looking to minimize water retention and improve overall health. Sodium, a mineral commonly found in table salt and processed foods, plays a significant role in fluid balance within the body. When consumed in excess, sodium can lead to increased water retention, making it essential to monitor and reduce intake for optimal well-being.
Processed foods are notorious for their high sodium content. Items such as canned soups, frozen meals, and packaged snacks often contain substantial amounts of sodium, which can contribute to bloating and discomfort. To combat this, individuals should focus on incorporating fresh, whole foods into their diets. These foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, typically contain lower levels of sodium and are rich in essential nutrients.
One effective way to reduce sodium intake is by reading food labels carefully. Many products may contain hidden sodium, even those marketed as “healthy.” By choosing options with lower sodium content, individuals can significantly decrease their overall intake. Additionally, using herbs and spices to flavor meals can provide taste without the added sodium, making it easier to enjoy food while maintaining a healthier diet.
Another beneficial approach is to prepare meals at home. Cooking from scratch allows for better control over the ingredients used, making it simpler to limit sodium levels. Experimenting with different cooking techniques, such as grilling, steaming, or roasting, can enhance flavors without relying on salt. Incorporating a variety of herbs and spices can transform a dish, providing depth and richness without the need for additional sodium.
It’s also important to stay hydrated. Drinking adequate amounts of water can help flush out excess sodium from the body. Surprisingly, increasing water intake can signal the kidneys to release stored fluids, counteracting the effects of high sodium consumption. Therefore, ensuring proper hydration not only supports overall health but also aids in reducing water retention.
Incorporating diuretic foods into the diet can further assist in minimizing water retention. Foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and celery have natural diuretic properties, helping to promote urine production and reduce fluid buildup. Including these foods in daily meals can provide both hydration and a natural way to combat water retention.
Moreover, being mindful of sodium sources during dining out is crucial. Restaurants often use salt liberally in their dishes, so requesting meals to be prepared with less salt or on the side can help manage sodium intake. Opting for grilled or steamed options instead of fried can also be beneficial, as these methods typically require less added salt.
In summary, reducing sodium intake is essential for minimizing water retention and promoting better health. By focusing on fresh, whole foods, reading labels, preparing meals at home, and staying hydrated, individuals can take significant steps towards achieving a healthier balance in their bodies. Implementing these strategies not only aids in reducing water weight but also contributes to overall well-being.
Incorporating Diuretic Foods
Certain foods act as natural diuretics, assisting the body in flushing out excess water. By incorporating these into your diet, you can effectively accelerate the process of losing water weight. Understanding the role of diuretic foods is essential for anyone looking to manage their weight and overall health.
What Are Diuretic Foods?
Diuretic foods are those that promote the production of urine, helping to eliminate excess fluid from the body. These foods can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing water retention due to various factors such as diet, hormonal changes, or sedentary lifestyles. By including diuretic foods in your meals, you can enhance your body’s natural ability to maintain a healthy fluid balance.
Top Diuretic Foods to Include in Your Diet
- Cucumbers: Known for their high water content, cucumbers are excellent for hydration and have mild diuretic properties.
- Watermelon: This refreshing fruit not only hydrates but also contains compounds that can promote urination.
- Celery: Rich in potassium and sodium, celery can help balance fluids and promote diuresis.
- Asparagus: Asparagus contains asparagine, an amino acid that acts as a natural diuretic, helping to flush out excess fluids.
- Beets: Beets are not only nutritious but also enhance kidney function and promote urination.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can stimulate digestion and promote fluid elimination.
- Green Tea: This popular beverage contains caffeine and antioxidants that can enhance diuretic effects.
How Diuretic Foods Aid in Weight Loss
Incorporating diuretic foods into your diet can help you shed water weight quickly. When your body retains excess fluids, it can lead to a bloated appearance and discomfort. By consuming diuretic foods, you can promote the elimination of this excess water, leading to a more toned and defined look.
Combining Diuretic Foods with a Balanced Diet
While diuretic foods can be beneficial, they should be part of a balanced diet. Pairing these foods with a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while effectively managing water retention. For example, a salad featuring cucumbers, beets, and a light dressing can be both refreshing and diuretic.
Hydration and Its Importance
Interestingly, consuming diuretic foods should be complemented with adequate hydration. Drinking plenty of water signals your body to release stored fluids, counteracting water retention. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, especially if you are incorporating diuretic foods into your meals.
Conclusion
Incorporating diuretic foods into your diet can be an effective strategy for managing water weight. By understanding the benefits of these foods and combining them with a healthy lifestyle, you can achieve your weight loss goals while promoting overall health. Remember, moderation and balance are key to maintaining a healthy body and preventing excessive fluid retention.

The Role of Hydration
is a fundamental aspect of maintaining overall health and well-being. Hydration not only supports vital bodily functions but also plays a significant role in managing water weight. Understanding how hydration affects fluid balance can empower individuals to make informed choices that promote a healthier lifestyle.
When we discuss hydration, it’s essential to recognize its importance in fluid balance. The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, which is crucial for processes such as digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation. Without adequate hydration, the body can struggle to maintain this balance, leading to various health issues, including water retention.
Ironically, one of the most effective ways to combat water retention is to increase water intake. Drinking more water can signal the body to release stored fluids, which can help reduce bloating and discomfort associated with excess water weight. This may seem counterintuitive, but when the body is adequately hydrated, it no longer feels the need to hold onto extra water.
- Benefits of Increased Water Intake:
- Promotes kidney function: Adequate hydration supports the kidneys in filtering waste and excess fluids from the bloodstream.
- Aids digestion: Water is essential for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients effectively.
- Enhances skin health: Proper hydration can improve skin elasticity and reduce dryness.
Moreover, hydration can significantly enhance the effectiveness of exercise routines. Regular physical activity increases sweat production, which is a natural way for the body to lose excess water. However, to maximize these benefits, it’s crucial to maintain hydration levels before, during, and after workouts.
- Hydration and Exercise:
- Pre-exercise hydration: Drinking water before a workout prepares the body for physical exertion and helps prevent dehydration.
- During exercise: Sipping water throughout the workout can replace lost fluids and maintain performance levels.
- Post-exercise recovery: Rehydrating after exercise is vital for recovery and helps restore fluid balance.
Incorporating diuretic foods into your diet can also support hydration while promoting fluid loss. Foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and celery have high water content and can help flush out excess fluids from the body. Additionally, these foods provide essential vitamins and minerals, contributing to overall health.
To further enhance hydration efforts, consider the following practical tips:
- Set hydration goals: Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, adjusting based on activity levels and climate.
- Flavor your water: If plain water feels monotonous, infuse it with fruits, herbs, or citrus for added flavor and nutrients.
- Track your intake: Use apps or journals to monitor water consumption and ensure you meet daily goals.
In conclusion, understanding the role of hydration in managing water weight is crucial for anyone looking to improve their health. By increasing water intake, recognizing the benefits of hydration, and incorporating healthy habits, individuals can effectively manage water retention and support overall well-being.
Benefits of Increased Water Intake
When it comes to maintaining optimal health and achieving weight loss goals, hydration plays a pivotal role. Many people overlook the importance of drinking enough water, but it can significantly impact bodily functions and overall well-being. This section will delve into the and how it can help combat water retention.
Water retention, or edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body’s tissues. This can lead to bloating and discomfort. One of the most effective ways to manage this condition is by increasing your water consumption. When you drink sufficient water, your body receives a signal to release stored fluids, thereby counteracting water retention.
Increased water intake supports kidney function by helping to flush out toxins and waste products. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating fluid balance in the body. When adequately hydrated, they can efficiently filter out excess sodium and other substances that contribute to water retention. This process not only reduces bloating but also enhances overall metabolic function.
Drinking more water can also aid in weight loss. Sometimes, our bodies confuse thirst for hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking. By staying hydrated, you can help curb unnecessary cravings, making it easier to stick to your dietary goals. Additionally, water has a natural appetite-suppressing effect, allowing you to feel fuller with fewer calories.
Proper hydration is essential for optimal physical performance. When exercising, your body loses water through sweat, and replenishing those fluids is crucial. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, decreased coordination, and muscle cramps. By maintaining adequate hydration, you can improve your stamina and endurance, allowing for more effective workouts that contribute to weight loss.
Another benefit of drinking enough water is its positive effect on skin health. Dehydration can lead to dry, flaky skin and exacerbate conditions like eczema. On the other hand, proper hydration helps to maintain skin elasticity and a youthful appearance. Keeping your skin well-hydrated can also help in reducing the appearance of puffiness and swelling associated with water retention.
In addition to drinking water, incorporating diuretic foods into your diet can further enhance fluid balance. Foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and celery are not only hydrating but also help promote urination, assisting the body in expelling excess water. Combining these foods with increased water intake creates a synergistic effect that can significantly reduce water retention.
Staying hydrated is also linked to improved mood and cognitive function. Dehydration can cause irritability and fatigue, making it harder to maintain a positive mindset. By ensuring you drink enough water throughout the day, you can enhance your overall mood, making it easier to stick to your health and fitness goals.
- Carry a reusable water bottle to track your intake.
- Set reminders on your phone to drink water at regular intervals.
- Infuse your water with fruits and herbs for added flavor.
- Consume water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables.
In conclusion, increasing your water intake can have profound effects on your body, from reducing water retention to enhancing overall health. By understanding the importance of hydration and implementing practical strategies to increase your water consumption, you can support your weight loss efforts and promote a healthier lifestyle.
Hydration and Exercise
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining optimal health and can play a significant role in weight management. When combined with regular exercise, hydration can significantly enhance the body’s ability to regulate fluids and promote overall well-being. This section delves into the intricate relationship between hydration and exercise, emphasizing their combined effects on losing water weight.
Understanding the Link Between Hydration and Exercise
Hydration is crucial for maintaining bodily functions, especially during physical activity. When you engage in exercise, your body temperature rises, leading to increased sweating. This process not only cools the body but also helps in expelling excess water. By staying properly hydrated, you can improve your performance and enhance the effectiveness of your workouts.
The Science Behind Sweating and Water Loss
- When you sweat, your body loses water and electrolytes, which are vital for various physiological processes.
- Regular physical activity increases blood circulation, which can help in the efficient transport of nutrients and waste products, further aiding in fluid balance.
- Hydration supports kidney function, enabling the body to flush out excess sodium and water, thereby reducing water retention.
Benefits of Combining Hydration with Exercise
Integrating proper hydration with your exercise routine can amplify the effects of both, leading to enhanced performance and quicker results in water weight loss. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Athletic Performance: Adequate hydration ensures that your muscles receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen, enhancing endurance and strength during workouts.
- Enhanced Recovery: Post-exercise hydration aids in muscle recovery, reducing soreness and fatigue, which allows for more consistent training sessions.
- Effective Temperature Regulation: Staying hydrated helps maintain a stable body temperature, preventing overheating during intense workouts.
Practical Tips for Staying Hydrated During Exercise
To maximize the benefits of hydration while exercising, consider the following tips:
1. Drink water before, during, and after your workouts.2. Monitor your hydration levels by checking the color of your urine; pale yellow indicates proper hydration.3. Incorporate electrolyte-rich drinks if you engage in prolonged or intense exercise sessions.4. Set reminders to drink water regularly throughout the day, especially if you tend to forget.
Choosing the Right Hydration Strategy
The type of hydration strategy you choose should align with your exercise intensity and duration. For moderate activities, plain water is typically sufficient. However, for longer or more intense workouts, consider beverages that contain electrolytes to replenish lost minerals.
Conclusion
Incorporating hydration into your exercise routine is not just beneficial but essential for achieving optimal results in water weight loss. By understanding the relationship between hydration and physical activity, you can create a balanced approach that enhances your overall health and fitness journey.
Physical Activity and Water Weight Loss
Engaging in regular exercise is a highly effective strategy for losing water weight. When it comes to shedding excess fluid, different types of workouts can yield varying results in fluid loss, making it essential to choose the right exercise regimen. This section delves into the connection between physical activity and water weight loss, highlighting the benefits of various exercise types and how they contribute to fluid balance.
Exercise stimulates the body’s metabolic processes and enhances circulation, which can lead to increased sweating and, consequently, fluid loss. During physical activity, the body releases stored water through perspiration, helping to reduce bloating and water retention. This process is particularly noticeable during aerobic exercises, where the heart rate elevates, and the body works harder to cool itself.
- Running: One of the most effective forms of aerobic exercise, running can lead to significant water loss within a short period. The intensity and duration of the run will determine the amount of fluid expelled through sweat.
- Cycling: Whether on a stationary bike or cycling outdoors, this activity promotes cardiovascular health and aids in fluid loss.
- Swimming: While it may seem counterintuitive, swimming can also help reduce water weight. The buoyancy of water allows for a full-body workout that can lead to sweating, especially in heated pools.
While strength training may not produce immediate water loss like aerobic exercises, it plays a crucial role in long-term weight management. Building muscle increases the body’s resting metabolic rate, which can enhance overall fluid balance. As muscle mass increases, the body becomes more efficient at using energy and expelling excess water.
HIIT combines short bursts of intense exercise with rest periods, making it an effective way to burn calories and lose water weight rapidly. This type of training elevates the heart rate significantly, leading to increased sweating and fluid loss. Additionally, HIIT workouts can be completed in a shorter time frame, making them a convenient option for those with busy schedules.
To maximize the benefits of exercise for water weight loss, consistency is essential. Incorporating a variety of workouts into your routine can prevent plateaus and keep the body engaged. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week.
While it may seem contradictory, staying hydrated is crucial for effectively losing water weight. Drinking adequate amounts of water can help the body release stored fluids, counteracting water retention. Furthermore, proper hydration supports overall performance during workouts, allowing individuals to exercise more effectively and safely.
In addition to structured workouts, incorporating more movement into daily life can also aid in losing water weight. Simple activities such as walking, taking the stairs, or engaging in recreational sports can contribute to overall physical activity levels. These small changes can make a significant difference in fluid balance and overall health.
In conclusion, engaging in regular exercise is a multifaceted approach to losing water weight. By understanding the different types of workouts and their effects on fluid loss, individuals can tailor their fitness routines to achieve optimal results. Remember, consistency, hydration, and a balanced approach to physical activity are essential for success in managing water weight.
Aerobic Exercise for Quick Results
Aerobic exercises, encompassing activities like running, cycling, and swimming, are not only effective for enhancing cardiovascular health but also serve as powerful tools for rapid water weight loss. When engaging in these activities, the body generates heat, leading to increased sweating and, consequently, immediate fluid loss.
Understanding how aerobic exercises impact fluid balance is crucial for anyone looking to shed excess water weight quickly. During aerobic workouts, the heart rate elevates, and the body requires more oxygen, prompting an increase in perspiration. This natural response can lead to a noticeable decrease in water retention.
Incorporating aerobic activities into your fitness regime can yield swift results. For instance, a 30-minute run can result in a significant amount of sweat loss, depending on factors such as temperature and humidity. Similarly, cycling at a moderate to vigorous intensity can also encourage the body to release stored fluids.
- Types of Aerobic Exercises:
- Running: Ideal for burning calories and promoting sweat loss.
- Cycling: Engaging and effective, whether on a stationary bike or outdoors.
- Swimming: A low-impact option that still promotes sweating, especially in warm water.
Moreover, the benefits of aerobic exercise extend beyond immediate water loss. Regular participation in these activities can enhance metabolic rate and improve overall body composition. As muscle mass increases, the body becomes more efficient at burning calories, even at rest.
To maximize the benefits of aerobic exercise for water weight loss, consider the following tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Ironically, drinking water before and after workouts can help maintain fluid balance and reduce retention.
- Mix Intensity Levels: Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your routine to boost sweat production and calorie burn.
- Consistency is Key: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week to see significant results.
In addition to structured workouts, lifestyle factors play a role in the effectiveness of aerobic exercises. For example, ensuring adequate rest and recovery can prevent overtraining, which may lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to water retention. Furthermore, managing stress levels through practices like yoga or meditation can enhance the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance.
In conclusion, incorporating aerobic exercises into your routine is a highly effective strategy for achieving quick water weight loss. By understanding the mechanisms behind sweat loss and combining these exercises with healthy lifestyle choices, you can optimize your results and improve your overall well-being.
Strength Training and Water Loss
Strength training is often overlooked when discussing weight loss strategies, particularly regarding water weight. While it may not yield immediate results in terms of fluid loss, the benefits of strength training extend far beyond the scale. By focusing on building muscle, individuals can enhance their metabolism, which plays a critical role in long-term weight management.
When we engage in strength training, we stimulate muscle fibers, leading to muscle growth and increased strength. This process, known as muscle hypertrophy, requires energy, which means the body burns more calories even at rest. This increase in metabolic rate is essential for anyone looking to maintain a healthy weight over time.
Moreover, muscle tissue is denser than fat, which means that as you gain muscle and lose fat, your weight on the scale may not change dramatically. This can lead to frustration for those solely focused on immediate results. However, the real victory lies in the body composition changes that occur. A higher muscle mass increases the body’s ability to burn calories, contributing to more effective long-term weight management.
In addition to boosting metabolism, strength training can also influence water retention. When you begin a strength training program, your muscles may retain water as they repair and grow. This initial increase in water weight can be misleading, but it is a natural part of the muscle-building process. Over time, as your body adapts to the training, you may notice a decrease in this water retention, contributing to a leaner appearance.
Furthermore, incorporating strength training into your routine can improve overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. It enhances bone density, improves joint function, and boosts mental health by releasing endorphins during workouts. These benefits are crucial for maintaining a balanced lifestyle and can indirectly support water weight loss efforts.
| Benefits of Strength Training | Impact on Water Weight |
|---|---|
| Increased Muscle Mass | May lead to temporary water retention |
| Boosted Metabolism | Promotes long-term weight management |
| Improved Bone Density | Reduces risk of osteoporosis |
| Enhanced Mental Health | Supports overall wellness |
To maximize the benefits of strength training for water weight loss, consider the following strategies:
- Consistency is Key: Aim for at least two to three strength training sessions per week to see results.
- Focus on Compound Movements: Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses engage multiple muscle groups, enhancing calorie burn.
- Hydrate Properly: Maintaining hydration helps manage water retention and supports muscle recovery.
- Pair with Cardio: Combining strength training with aerobic exercises can enhance overall weight loss and fluid balance.
In summary, while strength training may not produce immediate water loss, its role in building muscle is invaluable for enhancing metabolism and promoting long-term weight management. By understanding the benefits of strength training and incorporating it into a comprehensive fitness routine, individuals can achieve their weight loss goals more effectively.

Additional Lifestyle Adjustments
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly enhance your efforts to lose water weight. While dietary adjustments and exercise routines are essential, simple modifications to your daily habits can lead to substantial improvements in your body’s fluid balance. Below are several effective strategies to consider.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity is crucial. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can help promote sweating and reduce water retention.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Sleep is vital for overall health and can influence fluid balance. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow your body to recover and regulate hormones that affect fluid retention.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can lead to dehydration, prompting your body to retain water. Reducing your alcohol intake can help maintain a healthier fluid balance.
- Practice Mindfulness: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that lead to water retention. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels effectively.
Another important aspect is to monitor your sodium intake. High sodium levels can cause the body to hold onto water. By choosing fresh, whole foods over processed options, you can significantly reduce your sodium consumption, which can aid in losing water weight.
Additionally, it’s essential to stay hydrated. It may seem counterintuitive, but drinking more water can actually help your body release stored fluids. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and consider incorporating hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges into your diet.
Wearing comfortable clothing can also make a difference. Tight clothing may restrict circulation and contribute to bloating. Opt for loose-fitting attire that allows for better blood flow, which can help reduce the feeling of heaviness associated with water retention.
Furthermore, keeping a food diary can provide insights into your eating habits and their effects on water retention. Tracking your meals can help identify patterns, such as high-sodium days, and encourage healthier choices.
Lastly, consider consulting a healthcare professional if you notice persistent water retention. It can sometimes be a symptom of underlying health issues. A professional can offer tailored advice and support for managing your fluid balance effectively.
By implementing these lifestyle adjustments, you can create a more conducive environment for losing water weight. These changes, combined with dietary and exercise strategies, can lead to a healthier, more balanced body.
Avoiding Tight Clothing
When it comes to managing water retention and improving overall comfort, one often overlooked factor is the choice of clothing. can significantly impact both physical comfort and the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance. This article delves into the reasons why opting for loose-fitting attire can be beneficial for those experiencing bloating and water retention.
Wearing loose-fitting clothing is more than just a style choice; it can play a crucial role in enhancing circulation. Tight garments can constrict blood flow, leading to increased pressure in certain areas of the body. This pressure can exacerbate feelings of bloating and discomfort, particularly for individuals prone to water retention. By allowing for better circulation, loose clothing can help the body manage fluid levels more effectively.
In addition to improving circulation, loose clothing can also provide a greater sense of comfort. When the body retains excess water, it can lead to feelings of heaviness and tightness. Wearing comfortable, breathable fabrics can help alleviate these sensations, making it easier to go about daily activities without the distraction of discomfort. This is particularly important for individuals who are actively trying to lose water weight, as comfort can encourage more physical activity.
Moreover, the psychological aspect of wearing loose clothing should not be underestimated. Many people feel more confident and at ease in garments that do not cling to their bodies. This boost in self-esteem can lead to a more positive outlook on weight loss efforts, encouraging individuals to stick to their goals. When people feel good in what they wear, they are more likely to engage in social activities and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Another significant benefit of avoiding tight clothing is the reduction of skin irritation and chafing. Tight garments can cause friction against the skin, leading to discomfort and potential skin issues. Loose clothing allows the skin to breathe, reducing the risk of irritation and promoting overall skin health.
Additionally, wearing loose clothing can serve as a reminder to be mindful of one’s body and its needs. It encourages individuals to listen to their bodies and respond appropriately, whether that means taking a break, staying hydrated, or adjusting their diet. This mindfulness can be a powerful tool in managing water retention and promoting overall wellness.
Incorporating loose-fitting clothing into your wardrobe doesn’t have to mean sacrificing style. There are numerous fashionable options available that prioritize comfort without compromising on aesthetics. Look for natural fibers such as cotton, linen, or bamboo, which are not only breathable but also environmentally friendly.
In summary, avoiding tight clothing can lead to improved circulation, enhanced comfort, and a positive mindset, all of which are essential for managing water retention and supporting weight loss efforts. By making this simple yet effective change, individuals can create a more conducive environment for their bodies to thrive and maintain a healthy fluid balance.
Managing Stress Levels
is a vital aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly when it comes to managing water retention. High stress not only affects mental well-being but can also lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to excess fluid retention in the body. Understanding how stress impacts your body can help you implement effective stress management techniques to maintain a healthy fluid balance.
When you experience stress, your body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare your body for a “fight or flight” response, which can lead to various physiological changes. One of the significant effects of elevated cortisol levels is increased sodium retention in the kidneys, which can result in water retention. This process can make you feel bloated and heavier, impacting not just your physical appearance but also your overall comfort and health.
To combat the effects of stress on water retention, it is crucial to adopt effective stress management techniques. Here are some proven strategies:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can significantly reduce stress levels. These techniques help calm the mind and body, allowing for better hormonal regulation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a powerful stress reliever. Engaging in regular exercise helps release endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Moreover, it promotes better circulation, aiding in the reduction of water retention.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple deep breathing exercises can help lower stress levels quickly. Taking a few minutes to focus on your breath can activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing cortisol levels.
- Healthy Social Connections: Spending time with friends and family can provide emotional support, helping to alleviate stress. Building strong social networks contributes to better mental health.
- Balanced Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help stabilize your mood and energy levels. Avoiding high-sugar and high-fat foods can also prevent spikes in stress hormones.
Incorporating these strategies into your daily routine can help you manage stress effectively. It’s essential to recognize the signs of stress early and take proactive steps to address them. Not only will this improve your mental well-being, but it will also contribute to a healthier fluid balance in your body.
Additionally, consider the role of sleep in stress management. Poor sleep can exacerbate stress and hormonal imbalances, leading to further water retention. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your body’s recovery and hormonal regulation.
In conclusion, managing stress levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy fluid balance and preventing water retention. By implementing effective stress management techniques, you can positively impact your hormonal health and overall well-being. Remember, the journey to better health is a holistic one, and addressing stress is a significant step toward achieving your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is water weight?
Water weight refers to the excess fluid that your body retains, which can fluctuate due to various factors such as diet, hormonal changes, and physical activity. It’s important to understand this concept when trying to manage your weight effectively.
- How can I lose water weight quickly?
To lose water weight quickly, consider making dietary changes like reducing sodium intake and incorporating diuretic foods, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular aerobic exercises. These strategies can help your body release excess fluids efficiently.
- Does drinking more water help with water retention?
Absolutely! Ironically, drinking more water can signal your body to release stored fluids, helping to reduce water retention. Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy fluid balance in your body.
- Are there specific foods that can help reduce water retention?
Yes! Foods that act as natural diuretics, such as cucumbers, watermelon, and asparagus, can help flush excess water from your system. Incorporating these into your diet can accelerate the process of losing water weight.
- Can stress affect water retention?
Definitely! High stress levels can lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to water retention. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy fluid balance.












