This article explores the guidelines surrounding hydration before a fasting blood test, addressing common questions and providing expert insights to help you prepare effectively for your medical appointment.
Understanding Fasting Blood Tests
Fasting blood tests are crucial for obtaining accurate medical diagnoses. These tests measure various substances in your blood, such as glucose, cholesterol, and other markers, which can be influenced by recent food and drink intake. Therefore, fasting prior to the test is essential to ensure that the results reflect your baseline health status rather than temporary fluctuations caused by food consumption.
Why Is Fasting Important?
Fasting is important because it minimizes the variables that can affect test outcomes. When you eat or drink, your body processes these substances, leading to changes in your blood composition. For instance, glucose levels can spike after meals, which can mislead healthcare providers regarding your metabolic health.
The Role of Glucose Levels
After eating, glucose levels can vary significantly. If you have recently consumed food or beverages, your blood glucose readings may not accurately reflect your usual levels, which is particularly critical for diabetes testing. This inconsistency can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment plans.
How Food Affects Blood Sugar
Different foods can lead to varied blood sugar responses. For example, sugary foods can cause rapid increases in blood glucose, while high-fiber foods may result in a more gradual change. Understanding these effects can help you appreciate the necessity of fasting before tests.
The Importance of Consistency
Consistency in fasting practices is vital for reliable test results. If you routinely fast before tests, you will provide your healthcare provider with a clearer picture of your health trends over time.
Common Types of Fasting Blood Tests
Several blood tests require fasting, including lipid panels and glucose tolerance tests. These tests have specific fasting requirements, often necessitating a period of 8-12 hours without food or drink, except for water.
Can You Drink Water Before a Fasting Blood Test?
One of the most common inquiries is whether water consumption is allowed before a fasting blood test. The answer is generally yes; drinking water is typically permitted and even encouraged. Staying hydrated can help facilitate the blood draw and improve the accuracy of certain tests.
Hydration and Blood Test Accuracy
Proper hydration can positively influence blood test accuracy. Dehydration may lead to concentrated blood samples, which can skew results. Therefore, drinking water before your appointment is advisable, as it helps maintain blood volume and can make the blood draw easier.
Recommendations from Health Professionals
Health professionals commonly recommend drinking water before fasting blood tests. However, it is essential to avoid other beverages, especially those containing calories, caffeine, or artificial sweeteners, as they can interfere with test results.
What to Avoid Before a Fasting Blood Test
Understanding what to avoid is just as crucial as knowing what is allowed. Certain foods and beverages can compromise test outcomes. For instance, sugary drinks, alcohol, and even some herbal teas can affect results.
- Foods to Avoid: Avoid any solid foods, especially those high in sugar or fat.
- Beverages to Avoid: Stay away from coffee, tea (unless plain), and any drinks with calories.
Medications and Supplements
Some medications and supplements may also affect test results. It is important to consult your healthcare provider regarding any substances you are taking before your test. They can provide guidance on whether to continue or pause specific medications.
Preparing for Your Fasting Blood Test
Preparation is key to a successful blood test experience. Here are some practical tips:
- Scheduling Your Appointment: Choose a time for your test that aligns well with your fasting schedule, preferably in the morning.
- What to Expect During the Test: Understanding the testing process can alleviate anxiety. Typically, you will check in, provide identification, and then a healthcare professional will draw your blood.
Understanding Fasting Blood Tests
Fasting blood tests play a vital role in the realm of medical diagnostics. These tests are designed to measure various substances in the blood, providing crucial insights into a person’s health status. Understanding the significance of these tests can empower patients to take charge of their health and prepare adequately for their appointments.
What Are Fasting Blood Tests?
Fasting blood tests require patients to refrain from eating or drinking anything except water for a specified period, typically 8-12 hours, before the test. This fasting period is essential because it allows for a clear assessment of blood components without interference from recent food intake. Common tests that require fasting include:
- Lipid panels
- Glucose tests
- Comprehensive metabolic panels
Why Are Fasting Blood Tests Performed?
These tests are performed to evaluate various health conditions, including diabetes, cholesterol levels, and liver function. By ensuring that the body is in a fasting state, healthcare providers can obtain more accurate readings. For instance, after eating, glucose levels can spike, leading to misleading results that may indicate diabetes when none exists.
The Significance of Fasting
Fasting before a blood test is not merely a formality; it is a critical step in ensuring the accuracy of the results. When individuals consume food or beverages prior to testing, it can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar and lipid levels, skewing the results. This is particularly important for:
- Glucose Testing: Elevated glucose levels can indicate diabetes or prediabetes.
- Lipid Testing: Accurate cholesterol readings are essential for assessing cardiovascular health.
Moreover, fasting ensures that the body is in a baseline state, which is crucial for consistent and reliable results. Consistency in fasting practices can lead to improved health monitoring over time.
How Long Should You Fast?
Most fasting blood tests require an overnight fast of 8-12 hours. However, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions regarding fasting duration. This ensures that the results are not only accurate but also relevant to your health concerns.
Preparing for Your Fasting Blood Test
Preparation is key to a successful fasting blood test. Here are some practical tips:
- Schedule Wisely: Choose a time for your test that aligns with your daily routine, preferably in the morning after an overnight fast.
- Stay Hydrated: While fasting, it’s generally allowed to drink water. Staying hydrated can facilitate the blood draw and improve overall comfort.
- Avoid Strenuous Activity: Engaging in intense physical activity before the test can affect your results, particularly for glucose and lipid levels.
By understanding the importance of fasting blood tests and how to prepare for them, you can contribute to more accurate diagnoses and better health outcomes. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns regarding the fasting process or the tests themselves.
Why Is Fasting Important?
Fasting plays a critical role in ensuring the accuracy of blood tests. By refraining from food and drink for a specified period before testing, patients can provide healthcare professionals with reliable data necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment. This section delves into the reasons why fasting is not just a recommendation but a fundamental requirement for many blood tests.
One of the primary reasons fasting is essential is that it prevents recent food or drink intake from skewing test results. When we consume food, our bodies undergo various metabolic processes that can significantly alter the composition of our blood. For instance, glucose levels can spike after eating, which may lead to misleading results in tests designed to assess blood sugar control, such as those for diabetes.
Understanding the Impact of Food
- Food intake can lead to temporary increases in blood sugar levels, affecting diabetes diagnoses.
- High-fat meals can elevate triglyceride levels, which are crucial in assessing cardiovascular health.
- Different types of food can have varying impacts on the body, making it essential to fast for consistency.
Moreover, fasting helps maintain consistency in test results. When patients fast before tests, they minimize the variability that can arise from different dietary habits. This consistency is vital for healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on the results. For instance, a lipid panel test measures cholesterol levels, which can fluctuate based on recent meals. If a patient fasts, the results will be more reflective of their baseline levels.
The Role of Hydration
While fasting typically means abstaining from food and caloric beverages, the question of whether one can consume water arises frequently. Most healthcare professionals agree that drinking water is permissible and even encouraged before a fasting blood test. Staying hydrated can help facilitate blood draws and ensure that the blood sample is of adequate volume. However, it’s crucial to avoid flavored or sugary drinks, as these can still affect test results.
Common Fasting Blood Tests
Several blood tests require fasting to ensure accuracy. Among the most common are:
- Lipid Panel: Measures cholesterol levels and triglycerides.
- Glucose Test: Assesses blood sugar levels for diabetes management.
- Basic Metabolic Panel: Evaluates kidney function, electrolyte balance, and blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, fasting is a critical component of many blood tests, ensuring that results are not influenced by recent food or drink intake. By adhering to fasting guidelines, patients can help their healthcare providers obtain accurate and reliable data, leading to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
The Role of Glucose Levels
Understanding how glucose levels fluctuate after eating is crucial for individuals managing diabetes or undergoing blood tests. Glucose levels can vary significantly based on the type of food and drink consumed, making it essential to comprehend these effects for accurate diabetes testing.
When you consume food, especially carbohydrates, your body breaks it down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. This process can lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, often referred to as a postprandial spike. The extent of this spike can depend on several factors, including:
- Type of Food: Foods high in refined sugars and carbohydrates tend to cause a more significant increase in glucose levels compared to complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Portion Size: Larger portions can lead to higher glucose spikes, as more carbohydrates are available for conversion into glucose.
- Timing of Consumption: The timing of meals in relation to blood testing can significantly affect results, especially if testing occurs shortly after eating.
For those with diabetes, understanding how different foods affect glucose is vital for effective management. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help identify patterns in glucose fluctuations, allowing for better dietary choices and insulin management. For instance, individuals may notice that consuming a meal high in simple sugars leads to a quick rise in glucose levels, while a meal rich in fiber may result in a more gradual increase.
Moreover, beverages can also influence glucose readings. Drinks containing sugar, such as sodas or fruit juices, can cause immediate spikes in blood sugar. In contrast, water is generally considered safe and does not affect glucose levels, making it a suitable option for hydration before a fasting blood test.
It’s important to maintain a consistent routine when it comes to meal timing and composition, particularly before fasting blood tests. Consistency helps ensure that test results are reliable and can be accurately interpreted by healthcare providers. If dietary habits fluctuate significantly, it may lead to misleading test results, complicating diabetes management.
In conclusion, understanding the role of glucose levels and how they are influenced by food and drink is essential for effective diabetes testing and management. By being mindful of what is consumed prior to testing, individuals can achieve more accurate readings, leading to better health outcomes.
How Food Affects Blood Sugar
When it comes to managing health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk, understanding is crucial. The types of food consumed can lead to significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels, influencing test results and overall well-being. This section delves into the various categories of food and their impact on glucose levels.
Different foods can cause varying responses in the body. For instance, carbohydrates are one of the primary macronutrients that directly affect blood sugar. Foods high in simple sugars, such as candies and sugary drinks, can lead to rapid spikes in glucose levels. In contrast, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains and legumes, are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar.
Proteins and fats also play a role, albeit indirectly. While they do not cause immediate spikes in blood sugar, the type and amount consumed can influence insulin sensitivity over time. For example, a diet high in saturated fats may impair insulin function, leading to higher blood sugar levels in the long run. On the other hand, healthy fats, like those found in avocados and nuts, can promote better metabolic health when consumed in moderation.
| Food Type | Blood Sugar Impact |
|---|---|
| Simple Carbohydrates | Rapid spikes in blood sugar |
| Complex Carbohydrates | Gradual increase in blood sugar |
| Proteins | Minimal immediate effect; can improve insulin sensitivity |
| Healthy Fats | May support metabolic health |
Additionally, fiber-rich foods are essential for blood sugar management. Foods high in fiber, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, can slow down the absorption of sugar, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Incorporating these foods into your diet can be beneficial, especially for those monitoring their glucose levels.
- High-Fiber Foods: Oats, beans, lentils, and vegetables.
- Low-Glycemic Index Foods: Quinoa, sweet potatoes, and most fruits.
- Processed Foods: Generally should be avoided as they can lead to unpredictable blood sugar spikes.
Moreover, the timing of food intake can also affect blood sugar levels. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help maintain steadier glucose levels compared to large, infrequent meals that can lead to spikes. It’s advisable to monitor how different foods affect your body and adjust your diet accordingly.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between food and blood sugar is vital for anyone looking to maintain healthy glucose levels. By making informed choices about the types of food consumed and their timing, individuals can better manage their blood sugar and improve overall health.
The Importance of Consistency
Maintaining consistent fasting practices is vital for achieving accurate and reliable results in fasting blood tests. When patients adhere to a regular fasting schedule, it minimizes variables that could skew test outcomes. This section will explore how consistency in fasting leads to more reliable test results and why it is essential for effective health monitoring.
Fasting blood tests are designed to measure specific markers in the bloodstream, such as glucose and cholesterol levels. These markers can be significantly influenced by what you consume prior to the test. Therefore, adhering to a consistent fasting routine ensures that the body is in a similar state for each test, allowing for accurate comparisons over time.
- Regular Timing: Fasting at the same time each day or week can help standardize results. For instance, if a patient typically fasts overnight and schedules their test in the morning, this routine can yield more consistent glucose readings.
- Duration of Fasting: Consistency in the duration of fasting—typically 8-12 hours—ensures that the body is adequately prepared for testing. Variations in fasting duration can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar and lipid levels.
- Dietary Habits: Maintaining a consistent diet leading up to the fasting period can also play a crucial role. Sudden changes in diet can affect metabolic processes and, consequently, test results.
Moreover, the psychological aspect of consistency should not be overlooked. Establishing a routine can reduce anxiety associated with medical tests. Patients who are familiar with their fasting schedule may feel more at ease when they arrive for their blood tests, contributing to a smoother experience overall.
Research indicates that variations in fasting practices can lead to discrepancies in test results, which may result in misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment plans. For instance, a study published in a reputable medical journal highlighted that inconsistent fasting can lead to erroneous glucose readings, potentially affecting diabetes management.
In addition to the physiological benefits, consistent fasting practices can enhance patient-provider communication. When patients are diligent about their fasting routines, they can provide healthcare providers with more reliable data, enabling more informed decision-making regarding treatment plans.
Ultimately, the goal of fasting blood tests is to obtain the most accurate information possible about an individual’s health status. By maintaining a consistent fasting routine, patients can help ensure that their test results reflect their true health condition, facilitating better healthcare outcomes.
In summary, the importance of consistency in fasting practices cannot be overstated. It is not merely about abstaining from food and drink; it encompasses a holistic approach to health management. By establishing and adhering to a regular fasting schedule, patients can significantly improve the reliability of their fasting blood test results, leading to more effective monitoring and treatment of their health conditions.
Common Types of Fasting Blood Tests
When it comes to health assessments, fasting blood tests play a pivotal role in providing accurate diagnostic information. Understanding the different types of fasting blood tests is essential for anyone preparing for a medical evaluation. This section will delve into the most common fasting blood tests, including their specific fasting requirements, to help you be well-informed before your appointment.
- Lipid Panel: This test measures the levels of various types of fats in your blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides. Fasting for at least 9-12 hours prior to the test is typically required to ensure accurate results. Consuming food can significantly alter lipid levels, leading to misleading interpretations.
- Glucose Test: Often used to diagnose diabetes or prediabetes, this test measures blood sugar levels. A fasting period of 8-12 hours is generally recommended. Eating or drinking anything other than water can cause spikes in glucose levels, which may affect the diagnosis.
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP): This extensive blood test assesses various metabolic functions, including liver and kidney health. Patients are usually advised to fast for 10-12 hours to ensure that the test results reflect their baseline metabolic state without interference from recent food intake.
- Liver Function Tests: These tests evaluate the health of your liver by measuring enzymes and proteins in the blood. Fasting for 8-12 hours is often recommended to provide the most accurate assessment of liver function, as food can influence enzyme levels.
- Thyroid Function Tests: While some thyroid tests may not require fasting, specific tests that measure hormone levels often recommend fasting for optimal accuracy. It is best to consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions.
Each of these tests has unique fasting requirements, and adhering to them is crucial for obtaining reliable results. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications that might influence test outcomes.
In summary, understanding the types of fasting blood tests and their specific requirements is vital for anyone preparing for a medical evaluation. By following the fasting guidelines, you can ensure that your test results are accurate and reflective of your true health status.

Can You Drink Water Before a Fasting Blood Test?
When preparing for a fasting blood test, one of the most frequently asked questions is whether water consumption is permissible. This section aims to clarify the guidelines regarding water intake before testing, offering insights to ensure you are well-informed and prepared for your medical appointment.
Understanding the Guidelines
Typically, healthcare providers recommend that you stay hydrated by drinking water before a fasting blood test. Water does not contain calories or sugar, which means it does not interfere with the test results. However, it is essential to check with your healthcare provider, as some specific tests may have different requirements.
Why Hydration Matters
Staying hydrated is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved Blood Flow: Adequate hydration can help improve blood flow, making it easier for healthcare professionals to draw blood.
- Accurate Results: Water can help ensure that your blood sample accurately reflects your body’s state, especially in tests related to kidney function or electrolyte levels.
- Reduced Discomfort: Being well-hydrated may reduce discomfort during the blood draw.
Expert Recommendations
Experts generally agree that drinking water before a fasting blood test is acceptable. According to the American Association for Clinical Chemistry, water is usually the only fluid that is allowed during the fasting period. It is vital to avoid any beverages that contain sugar, caffeine, or artificial sweeteners, as these can alter your test results.
What to Avoid
While water is permitted, there are several things you should avoid:
- Caffeinated Beverages: Coffee and tea can affect hydration levels and may also influence test results.
- Juices and Soft Drinks: These drinks contain sugars and calories that can interfere with the accuracy of your blood test.
- Alcohol: Consuming alcohol can significantly impact your blood test results and should be avoided at least 24 hours prior to testing.
Final Thoughts
In summary, drinking water before a fasting blood test is generally permitted and can be beneficial. However, it is essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure the most accurate results. Always communicate with your medical team if you have any doubts or questions regarding your fasting protocol.
Hydration and Blood Test Accuracy
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, and its importance extends to the realm of medical testing, particularly fasting blood tests. Staying adequately hydrated before a blood test can significantly impact the accuracy of the results. In this section, we will explore how hydration affects blood test accuracy and why it is generally permissible to drink water prior to the test.
When preparing for a fasting blood test, many individuals wonder about the guidelines regarding water consumption. The general consensus among healthcare professionals is that drinking water is not only allowed but encouraged. Proper hydration can help facilitate the blood draw and improve the quality of the sample.
Hydration levels can influence various parameters measured during blood tests. For instance, dehydration can lead to concentrated blood samples, which may skew the results of certain tests. When the body is dehydrated, the concentration of substances in the blood, such as electrolytes and glucose, can become artificially elevated. This is particularly important for tests that evaluate kidney function and electrolyte balance.
- Electrolyte Levels: Dehydration can result in increased sodium and potassium levels, potentially leading to misleading interpretations of kidney function.
- Blood Viscosity: A lack of fluids can increase blood viscosity, making it more challenging for healthcare professionals to draw blood and potentially affecting the test results.
- Glucose Readings: In some cases, dehydration can cause a spike in blood glucose levels, which may complicate diabetes management and diagnosis.
Water consumption before a fasting blood test is widely accepted due to its neutral impact on test results. Unlike other beverages, water does not contain calories, sugars, or other compounds that could interfere with the accuracy of the tests. In fact, staying hydrated can help ensure that the blood sample collected is of high quality, allowing for more reliable results.
Many healthcare providers recommend drinking water prior to the test to help maintain hydration levels. It is important, however, to avoid any flavored or sweetened beverages, as these can introduce variables that may affect the test outcomes.
Experts suggest drinking at least one or two glasses of water in the hours leading up to your blood test. This not only helps with the blood draw but also promotes overall health and well-being. It is essential to listen to your body, as individual hydration needs can vary based on factors such as activity level, climate, and overall health.
In summary, staying hydrated before a fasting blood test is beneficial for both the patient and the healthcare provider. It can enhance the quality of the blood sample and minimize the risk of inaccurate test results. Always consult with your healthcare provider for specific instructions regarding hydration and preparation for your blood test, as they can provide tailored advice based on your unique health needs.
Recommendations from Health Professionals
When preparing for a fasting blood test, understanding the guidelines surrounding hydration is crucial. One common question that arises is whether it is permissible to drink water before the test. This section explores the regarding water consumption prior to a fasting blood test.
Healthcare providers generally agree that staying hydrated is not only allowed but can be beneficial before a fasting blood test. Water does not contain calories or sugar, meaning it does not interfere with the metabolic processes that fasting blood tests aim to measure. As a result, many experts encourage patients to drink water to ensure they are adequately hydrated. This can help facilitate the blood draw process by making veins more visible and easier to access.
However, opinions can vary among healthcare professionals. Some suggest limiting water intake to a few sips, particularly for tests that require strict fasting, such as lipid panels. These tests measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which can be affected by factors other than food intake. In such cases, health professionals may recommend that patients avoid excessive water consumption to ensure the most accurate results.
Another consideration is the timing of water consumption. Many healthcare providers advise patients to drink water only up to a few hours before the test. This approach helps to ensure that the body is in a fasting state while still allowing for hydration. It is essential to follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider, as they may have tailored recommendations based on individual health conditions or the type of blood test being performed.
In addition to hydration, patients are encouraged to pay attention to their overall pre-test preparation. This includes avoiding strenuous exercise and ensuring adequate rest the night before the test. These factors can also influence blood test results and contribute to a more accurate assessment of health.
For those who are unsure about how much water to drink, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the type of test and individual health needs. Overall, while hydration is generally encouraged, the approach may vary depending on the specific circumstances of the fasting blood test.
In summary, drinking water before a fasting blood test is typically permitted and can aid in the testing process. However, it is crucial to follow the guidance of healthcare professionals to ensure the most accurate results. By understanding the nuances of hydration and fasting, patients can better prepare for their blood tests and contribute to their overall health management.
What to Avoid Before a Fasting Blood Test
Preparing for a fasting blood test involves more than simply abstaining from food and drink; it also requires an understanding of what to avoid to ensure accurate results. Knowing which substances and activities can interfere with your test outcomes is crucial for obtaining reliable data that your healthcare provider can use for diagnosis and treatment.
Foods and Beverages to Steer Clear Of
Before undergoing a fasting blood test, it is essential to avoid certain foods and beverages that can skew your results. Here are some key items to exclude:
- High-Sugar Foods: Consuming sugary snacks or drinks can elevate your glucose levels, affecting diabetes-related tests.
- Fatty Foods: Foods rich in fats can alter lipid panels, leading to misleading cholesterol readings.
- Caffeinated Beverages: Coffee and energy drinks may impact blood pressure and glucose levels, potentially complicating your test results.
- Alcohol: Drinking alcohol before a test can significantly affect liver function tests and blood sugar levels.
Medications and Supplements
Many individuals overlook the influence of medications and supplements on blood test results. Here are some considerations:
- Prescription Medications: Some medications, such as steroids and diuretics, can impact test results. Always consult your healthcare provider about any prescriptions you are taking.
- Over-the-Counter Drugs: Common pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can affect liver enzymes and other test outcomes.
- Vitamins and Herbal Supplements: Certain supplements, particularly those containing high doses of vitamin C or herbal remedies, may interfere with laboratory tests.
Activities to Avoid
In addition to dietary restrictions, specific activities should also be avoided prior to your fasting blood test:
- Excessive Exercise: Strenuous workouts can lead to temporary changes in muscle enzymes and hormone levels, which may skew results.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can affect blood pressure and heart rate, potentially impacting cardiovascular tests.
- Stress: High-stress levels can alter hormone levels and blood pressure, which may influence various test outcomes.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before your test, always discuss with your healthcare provider about any specific restrictions or guidelines tailored to your health condition. This personalized advice can be invaluable in ensuring the accuracy of your blood test.
By understanding what to avoid before your fasting blood test, you can help ensure that your results are accurate and reflective of your true health status. This knowledge empowers you to take control of your health and helps your healthcare provider make informed decisions based on reliable data.
Foods and Beverages to Steer Clear Of
When preparing for a fasting blood test, it is crucial to understand which foods and beverages to avoid to ensure the accuracy of your results. Consuming certain items can significantly compromise the outcomes of the tests, leading to misleading information regarding your health. Below, we outline specific categories of foods and beverages that should be steered clear of prior to your appointment.
- High-Sugar Foods: Items such as candies, pastries, and sugary cereals can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, which can interfere with glucose testing.
- Fried and Greasy Foods: Foods that are high in fat can affect lipid levels and may lead to inaccurate cholesterol readings. Avoid fried foods like french fries and doughnuts.
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption can alter liver function and blood sugar levels, which may skew the results of various blood tests. It is advisable to avoid alcohol for at least 24 hours prior to testing.
- Caffeinated Beverages: Coffee, tea, and energy drinks can stimulate metabolism and affect hydration levels, potentially leading to skewed results. It’s best to avoid these drinks before your test.
- Fruit Juices: Even natural fruit juices can contain high levels of sugar that may affect blood glucose readings. Whole fruits should also be avoided for similar reasons.
- Processed Foods: Foods that are high in preservatives, artificial flavors, and colors can introduce variables that may impact test results. Stick to whole, unprocessed foods in the days leading up to your test.
- High-Carbohydrate Foods: Foods such as bread, pasta, and rice can lead to increased blood sugar levels. It is recommended to avoid these foods for at least 8-12 hours before your test.
In addition to food, it is important to consider beverages as well. While water is generally allowed and encouraged to stay hydrated, other drinks should be avoided:
- Soda and Soft Drinks: These beverages are often high in sugar and can lead to inaccurate glucose readings.
- Sports Drinks: Similar to sodas, sports drinks contain sugars and electrolytes that can affect test results.
- Milk and Dairy Products: Dairy can contain fats and sugars that may interfere with lipid and glucose tests.
By being aware of these foods and beverages, you can help ensure that your fasting blood test yields the most accurate results possible. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have any questions regarding your pre-test preparations.
Medications and Supplements
When preparing for a fasting blood test, it is crucial to consider the potential impact of medications and supplements on test results. Many individuals may not realize that certain substances can interfere with the accuracy of their blood tests, leading to misleading results. This section will explore which medications and supplements could affect your test outcomes and emphasize the importance of consulting with your healthcare provider.
Medications can have a significant impact on various blood test parameters. For instance:
- Antibiotics may alter liver enzyme levels.
- Blood thinners can affect coagulation tests.
- Cholesterol-lowering medications may influence lipid panel results.
It’s essential to inform your doctor about any prescription or over-the-counter medications you are taking, as they can provide guidance on whether you need to pause any treatment before your test.
Many people take vitamins and herbal supplements without considering their effects on blood tests. Some common supplements that may interfere include:
- Fish oil can raise triglyceride levels.
- Vitamin D may influence calcium levels.
- St. John’s Wort can affect liver enzymes and drug metabolism.
These substances can lead to inaccurate readings, which could result in unnecessary anxiety or misdiagnosis. Therefore, it is advisable to discuss any supplements you are taking with your healthcare provider prior to your fasting blood test.
Consulting your doctor is vital for several reasons:
- Personalized Advice: Your doctor can provide tailored recommendations based on your health history and the specific tests being performed.
- Accurate Interpretation: They can interpret test results in the context of your medication and supplement use, ensuring a more accurate diagnosis.
- Safety Considerations: Some medications may require adjustments before testing to avoid complications or inaccurate results.
To ensure the most accurate results possible, follow these guidelines:
- Disclose All Medications: Provide a complete list of all medications and supplements to your healthcare provider.
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to any specific instructions given by your doctor regarding medication use prior to the test.
- Consider Timing: If you need to stop taking a medication, discuss how long before the test this should occur.
By being proactive and communicating openly with your healthcare provider, you can minimize the risk of interference from medications and supplements, leading to more reliable test results.
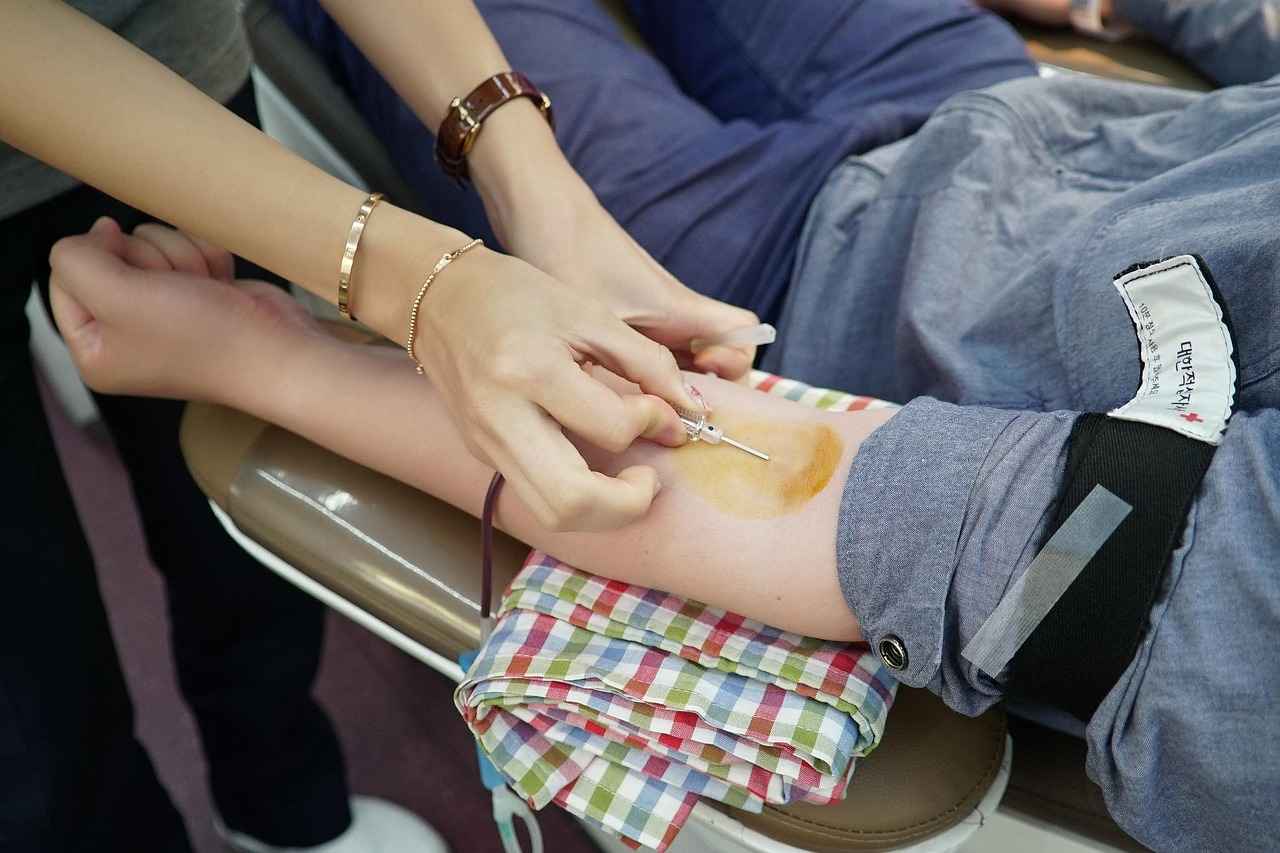
Preparing for Your Fasting Blood Test
Preparation is key to a successful blood test experience. Proper preparation can significantly impact the accuracy of your test results and make the process smoother. This section provides practical tips on how to prepare for your fasting blood test effectively, ensuring you arrive at your appointment feeling confident and informed.
First and foremost, it is essential to understand the fasting requirements for your specific blood test. Generally, fasting means refraining from all food and drink, except for water, for a specified period before the test—usually between 8 to 12 hours. Always confirm the exact requirements with your healthcare provider, as different tests may have varying guidelines.
- Stay Hydrated: While fasting typically restricts food intake, drinking water is often encouraged. Staying hydrated can help facilitate the blood draw and improve overall blood flow. Aim to drink plenty of water the day before your test and continue to hydrate on the morning of the test.
- Avoid Certain Foods: Prior to your fasting blood test, it is crucial to avoid high-fat, sugary, or processed foods. These can interfere with glucose and lipid levels, leading to inaccurate results. Stick to a light, healthy meal the night before, such as grilled chicken and vegetables.
- Review Medications: Some medications and supplements can affect test results. Consult your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking and whether you should pause them before your test. This is particularly important for medications that influence blood sugar levels.
- Plan Your Appointment Wisely: Schedule your blood test for a time when you can comfortably fast. Many people prefer morning appointments to minimize the duration of fasting overnight. This can help reduce discomfort and anxiety.
Additionally, it is beneficial to prepare mentally for your blood test. Understanding what to expect can alleviate anxiety. Familiarize yourself with the blood draw process, which typically involves a healthcare professional using a needle to collect a small sample of blood. The procedure is quick and generally causes minimal discomfort.
On the day of your test, ensure you wear comfortable clothing with easy access to your arms, as this will make the process smoother. Bring along any required identification and insurance information, as well as a list of any medications you are currently taking.
Lastly, after the test, it is important to follow any post-test instructions provided by your healthcare provider. This may include dietary recommendations or when to expect your results. Remember, proper preparation not only aids in obtaining accurate test results but also contributes to a more pleasant experience overall.
By following these practical tips, you can ensure that you are well-prepared for your fasting blood test, leading to more reliable outcomes and peace of mind.
Scheduling Your Appointment
When it comes to preparing for a fasting blood test, timing is crucial. The scheduling of your appointment can significantly influence the accuracy of your results and your overall experience. In this section, we will provide you with expert advice on how to choose the best time for your fasting blood test.
First and foremost, consider your daily routine. Many people find it easiest to schedule their blood tests in the early morning. This allows you to fast overnight, minimizing discomfort and making it easier to comply with the fasting requirements. Additionally, morning appointments can help you avoid the temptation to eat or drink before the test, as you can simply wake up, go to the appointment, and resume your normal routine afterward.
Another important aspect to consider is your medication schedule. If you are on medications that require food intake, consult with your healthcare provider about the best time to schedule your test. Some medications may need to be taken with food, while others might not be affected by fasting. Your doctor can provide tailored advice to ensure that your test results are not skewed by medication interactions.
It’s also essential to think about potential delays at the testing facility. If you schedule your appointment during peak hours, you may encounter longer wait times, which can be uncomfortable when you are fasting. Aim for times that are typically less busy, such as mid-morning or early afternoon, to reduce the likelihood of delays.
Moreover, consider any upcoming medical procedures or appointments that could interfere with your fasting blood test. If you have another medical appointment or procedure scheduled soon after, it may be wise to allow adequate time for fasting and recovery. This will ensure that you are not rushed and can focus on the test itself.
Lastly, don’t forget to prepare mentally for your appointment. Being well-informed about what to expect can alleviate anxiety and make the experience smoother. Familiarize yourself with the testing process, and ensure that you have all necessary documents ready for your visit. This preparation can help you feel more at ease and allow you to focus on the importance of the test.
In summary, choosing the right time for your fasting blood test involves careful consideration of your daily routine, medication schedules, potential delays, and other medical appointments. By planning ahead and following these expert recommendations, you can optimize your testing experience and ensure the most accurate results possible.
What to Expect During the Test
When preparing for a fasting blood test, understanding the testing process can significantly alleviate anxiety. Knowing what to expect can transform a potentially stressful experience into a more manageable one. This section outlines the entire journey from check-in to the blood draw, ensuring you feel informed and prepared.
Upon arrival at the lab or clinic, you will first check in at the reception. Make sure to bring any necessary documents, such as your identification and insurance information. After check-in, you may be asked to complete a brief medical history form, which helps the healthcare providers understand your background and any specific concerns you might have.
Once your paperwork is completed, you will wait in a designated area until a phlebotomist calls your name. The waiting time can vary, but it is typically short. During this time, it is perfectly normal to feel a bit anxious. To help ease your nerves, take deep breaths and remind yourself that this procedure is a routine part of maintaining your health.
When called, you will be escorted to a private area where the blood draw will take place. The phlebotomist will explain the procedure and may ask you a few questions to ensure you are comfortable. It is important to communicate any concerns or fears you might have; healthcare professionals are trained to help you feel at ease.
Next comes the actual blood draw. The phlebotomist will clean the area on your arm with an antiseptic wipe and apply a tourniquet to make your veins more prominent. After locating a suitable vein, they will insert a sterile needle to collect the required amount of blood. The sensation may be a quick pinch, but it typically lasts only a moment. If you are feeling particularly anxious, you can look away or engage in conversation with the phlebotomist to distract yourself.
Once the blood has been drawn, the phlebotomist will remove the needle and apply a small bandage to the site. They may also provide instructions on how to care for the area afterward, such as keeping it clean and avoiding heavy lifting for a short time. After the procedure, you will be free to leave, and the results of your test will usually be available within a few days, depending on the type of testing being conducted.
In summary, understanding the process of a fasting blood test can significantly reduce anxiety. From check-in to the blood draw, knowing what to expect helps you feel more in control and prepared. Remember, the healthcare professionals are there to assist you, so don’t hesitate to ask questions or express any concerns you may have during your visit.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I drink water before a fasting blood test?
Yes, you can usually drink water before a fasting blood test. Staying hydrated is important and won’t interfere with most test results. Just avoid anything other than plain water!
- How long should I fast before the test?
Typically, you should fast for at least 8 to 12 hours prior to your blood test. This means no food or drink, except for water, during that time.
- Will drinking water affect my blood test results?
No, drinking water is generally safe and can help ensure your veins are more visible for the blood draw. Just make sure to avoid any flavored or sugary drinks!
- What should I avoid before a fasting blood test?
Avoid all food and beverages except water. This includes coffee, tea, and alcohol, as they can skew your results. Also, check with your doctor about any medications you should avoid.
- Can I brush my teeth before the test?
It’s best to avoid brushing your teeth if you use toothpaste that contains sugar or flavoring, as this might affect the test results. If you must, use plain water only.












